Anterior cruciate ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Anterior cruciate ligament | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the right knee. Anterior cruciate ligament labeled at center left. | |
| Details | |
| From | lateral condyle of the femur |
| To | intercondyloid eminence of the tibia |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum cruciatum anterius |
| MeSH | D016118 |
| TA | A03.6.08.007 |
| FMA | 44614 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are also called cruciform ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint (analogous to the knee), based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament.[1] The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four main ligaments of the knee, providing 85% of the restraining force to anterior tibial displacement at 30 degrees and 90 degrees of knee flexion.[2]
Contents
1 Structure
2 Purpose
3 Clinical significance
3.1 Injury
3.2 Non-operative treatment of the ACL
3.3 Operative treatment of the ACL
3.4 ACL injuries in Women
4 Additional images
5 See also
6 References
7 External links
Structure[edit]
The ACL originates from deep within the notch of the distal femur. Its proximal fibers fan out along the medial wall of the lateral femoral condyle. There are two bundles of the ACL: the anteromedial and the posterolateral, named according to where the bundles insert into the tibial plateau. (The tibia plateau is a critical weight-bearing region on the upper extremity of the tibia). The ACL attaches in front of the intercondyloid eminence of the tibia, where it blends with the anterior horn of the lateral meniscus.
Purpose[edit]
These attachments allow the ACL to resist anterior translation and medial rotation of the tibia, in relation to the femur.
Clinical significance[edit]
Injury[edit]

MRI of anterior cruciate ligament tear
An ACL tear is one of the most common knee injuries, with over 100,000 tears occurring annually in the US. Most ACL tears are a result of a non-contact mechanism such as a sudden change in a direction causing the knee to rotate inward. As the knee rotates inward additional strain is placed on the ACL, since the femur and tibia, which are the two bones that articulate together forming the knee joint, move in opposite directions causing the ACL to tear. Most athletes will require reconstructive surgery on the ACL, in which the torn or ruptured ACL is completely removed and replaced with a piece of tendon or ligament tissue from the patient (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). Conservative treatment has poor outcomes in ACL injury since the ACL is unable to form a fibrous clot as it receives most of its nutrients from the synovial fluid which washes away the reparative cells making it difficult for new fibrous tissue to form. The two most common sources for tissue are the patellar ligament and the hamstrings tendon. The patellar ligament is often used, since bone plugs on each end of the graft are extracted which helps integrate the graft into the bone tunnels, during reconstruction. The surgery is arthroscopic, meaning that a tiny camera is inserted through a small surgical cut. The camera sends video to a large monitor so that the surgeon can see any damage to the ligaments. In the event of an autograft, the surgeon will make a larger cut to get the needed tissue. In the event of an allograft, in which material is donated, this is not necessary since no tissue is taken directly from the patient’s own body. The surgeon will drill a hole forming the tibial bone tunnel and femoral bone tunnel, allowing for the patient’s new ACL graft to be guided through. Once the graft is pulled through the bone tunnels, two screws are placed into the tibial and femoral bone tunnel. Recovery time ranges between one and two years or longer, depending if the patient chose an autograft or allograft. A week or so after the occurrence of the injury, the athlete is usually deceived by the fact that he/she is walking normally and not feeling much pain. This is dangerous as some athletes start resuming some of their activities such as jogging which, with a wrong move or twist, could damage the bones as the graft has not completely become integrated into the bone tunnels. It is important for the injured athlete to understand the significance of each step of an ACL injury to avoid complications and ensure a proper recovery.
Non-operative treatment of the ACL[edit]
The ACL can be treated non operatively with strengthening and rehabilitation when the ACL is not completely torn and the knee is still stable or if the patient is not doing activities requiring cutting and pivoting or similar actions. The mainstay of ACL non-operative treatment is strengthening of the muscles around the knee, especially the hamstrings. Focused therapy supervised by a physical therapist can be an effective way to accomplish this.[citation needed]
Operative treatment of the ACL[edit]
Anterior cruciate ligament surgery is a complex operation that requires expertise in the field of orthopedic and sports medicine. Many factors should be considered when discussing surgery including the athlete's level of competition, age, previous knee injury, other injuries sustained, leg alignment and graft choice. Occasionally, stimulation of the body's natural ability to heal the native ligament, called a “healing response”, is relied upon. More commonly, the ligament must be replaced by a graft from the patient's own tissue or tissue from a cadaver. Graft choice could be confusing, requiring expert counseling from a doctor.[citation needed]
Rehabilitation is crucial to any ACL surgery; complete recovery and return to sports or other activities typically takes six to nine months. Revision ACL surgery will often take nine months to more than a year. During this time, the physical therapist should guide the patient through the rehabilitation process. The early rehab, usually lasting around six weeks, focuses on maintaining full knee motion and preventing scar tissue. The second phase of rehab is directed toward regaining knee strength. Finally, activity-specific rehabilitation is administered. The rehabilitation program can also be composed of aggressive motions and weight-bearing exercises.[citation needed]
If the doctor recommends surgery for ACL, he or she may prescribe "prehab" before operating, as many studies have shown that inducing good motion before the surgery will benefit the patient during recovery.[citation needed]
A 2010 Los Angeles Times review of two medical studies discussed whether ACL reconstruction was advisable. One study found that children under 14 who had ACL reconstruction fared better after early surgery than those who underwent a delayed surgery. But for adults 18 to 35, patients who underwent early surgery followed by rehabilitation fared no better than those who had rehabilitative therapy and a later surgery.[3]
The first report focused on children and the timing of an ACL reconstruction. ACL injuries in children are a challenge because children have open growth plates in the bottom of the femur or thigh bone and on the top of the tibia or shin. An ACL reconstruction will typically cross the growth plates, posing a theoretical risk of injury to the growth plate, stunting leg growth or causing the leg to grow at an unusual angle.[4]
The second study noted in the L.A. Times piece focused on adults. It found no significant statistical difference in performance and pain outcomes for patients who receive early ACL reconstruction vs. those who receive physical therapy with an option for later surgery. This would suggest that many patients without instability, buckling or giving way after a course of rehabilitation can be managed non-operatively. However, the study points to the need for more extensive research, was limited to outcomes after two years and did not involve patients who were serious athletes.[3] Patients involved in sports requiring significant cutting, pivoting, twisting or rapid acceleration or deceleration may not be able to participate in these activities without ACL reconstruction. The randomized control study was originally published in the New England Journal of Medicine.[5]
ACL injuries in Women[edit]
Women have been known to suffer ACL injuries more frequently than men due to anatomical differences in their ACL compared to men. Current research attributes this finding to multiple factors that are still being studied. The synovial joint through which the anterior cruciate ligament passes, along with the length of the anterior cruciate ligament, is significantly smaller in women than in men. This makes it more susceptible to damage since the ACL is exposed to a higher level of strain in comparison to men. Along with these aspects, women tend to use their quadriceps muscle more often than their hamstring muscles which place additional strain on the ACL. Women also more commonly land with their knees bent inward when landing after a jump, adding more strain on the ACL to maintain stability in the knee. In addition, the quadriceps angle, or Q-angle, between the anterior superior iliac spine and patellar ligament may contribute to the predisposition of ACL tears, as females often have wider hips compared to males. There is some evidence that suggests since women are known to have larger Q-angles than their male counterparts, causing their knee to already be bent inward making them more susceptible to ACL tears.[7][citation needed]
Additional images[edit]
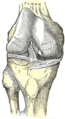
Right knee-joint, from the front, showing interior ligaments.

Left knee-joint from behind, showing interior ligaments.
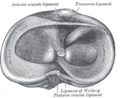
Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments.
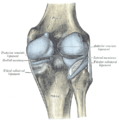
Capsule of right knee-joint (distended). Posterior aspect.
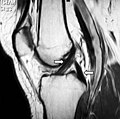
MRI shows normal signal of both cruciate ligaments (arrows).
Knee joint.Deep dissection. Anteromedial view.
See also[edit]
- Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Anterior drawer test
- Anterolateral ligament
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Medial collateral ligament
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- Unhappy triad
References[edit]
^ "Canine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease" (PDF). Melbourne Veterinary Referral Centre. pp. 1–2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2008. Retrieved September 8, 2009..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Ellison A, Berg E. Embryology, anatomy, and function of the anterior cruciate ligament. Orthop Clin North Am 1985;16:3-14. PubMed Abstract
^ ab Stein, Jeannine (2010-07-22). "Studies on ACL surgery". The Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on July 28, 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-23.
^ "ACL Tears: To reconstruct or not, and if so, when?". howardluksmd.com. Retrieved 2010-07-23.
^ Frobell, Richard B.; Roos, Ewa M.; Roos, Harald P.; Ranstam, Jonas; Lohmander, L. Stefan (2010). "A Randomized Trial of Treatment for Acute Anterior Crut Tears". New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (4): 331–342. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0907797. PMID 20660401.
External links[edit]
Anatomy photo:17:02-0701 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Extremity: Knee joint"
Anatomy figure: 17:07-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Superior view of the tibia."
Anatomy figure: 17:08-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Medial and lateral views of the knee joint and cruciate ligaments."
lljoints at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (antkneejointopenflexed)
Categories:
- Knee ligaments
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.488","walltime":"0.793","ppvisitednodes":{"value":2100,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":93301,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":3568,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":11,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":4,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":16506,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":2,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 683.240 1 -total"," 27.30% 186.521 1 Template:Infobox_ligament"," 26.49% 181.010 1 Template:Infobox_anatomy"," 24.10% 164.683 1 Template:Infobox"," 22.76% 155.475 1 Template:Reflist"," 15.07% 102.946 5 Template:Citation_needed"," 14.96% 102.189 2 Template:Cite_web"," 13.26% 90.582 5 Template:Fix"," 10.61% 72.475 1 Template:About"," 6.59% 45.019 10 Template:Category_handler"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.245","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":4967305,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1265","timestamp":"20181128171014","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"Anterior cruciate ligament","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_cruciate_ligament","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q611127","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q611127","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2004-04-06T01:35:05Z","dateModified":"2018-11-26T22:42:20Z","image":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/09/Knee_diagram.svg","headline":"type of cruciate ligament in the human knee"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":159,"wgHostname":"mw1250"});});







