ZygoteBody
ZygoteBody
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
ZygoteBody, formerly Google Body, is a web application by Zygote Media Group that renders manipulable 3D anatomical models of the human body. Several layers, from muscle tissues down to blood vessels, can be removed or made transparent to allow better study of individual body parts. Most of the body parts are labelled and are searchable.
Contents
1 Technology
2 History
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Technology[edit]
The human models are based on data from the Zygote Media Group. The website uses JavaScript and WebGL technology to display 3D images inside the web browser without requiring the installation of external browser plug-ins.[citation needed]
History[edit]
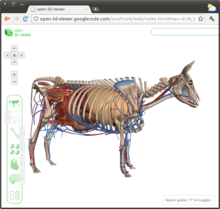
The Google Cow model, now part of the open-3d-viewer project
ZygoteBody was launched as Google Body on December 15, 2010. On April Fools' Day 2011, users were greeted with the anatomy of a cow on the home page.[1] The cow model is still available as part of the open-3d-viewer open source project.
As part of the wind down on Google Labs, it was announced that Google Body will be shut down but will continue to be maintained by Zygote as ZygoteBody. On October 13, 2011 the Google Body site was shut down. Then on January 9, 2012 ZygoteBody was launched and core code base (with the Google Cow model as a demo) was made available as an open source project called open-3d-viewer.[2]
See also[edit]
- Visible Human Project
- Google Health
- Anatomography
References[edit]
^ Chitu, Alex (April 1, 2011). "Google April Fools' Day 2011". Google Operating System unofficial blog. Retrieved January 27, 2012..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Zeiger, Roni (January 9, 2012). "Google Body becomes ZygoteBody; built on open source 3D viewer". Google Open Source blog. Retrieved January 27, 2012.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to ZygoteBody. |
- Official website
- open-3d-viewer
Categories:
- Anatomical simulation
- Google services
- Web applications
- Anatomy websites
- 2010 software
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.276","walltime":"0.428","ppvisitednodes":{"value":759,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":68081,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":942,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":12,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":2,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":5389,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":1,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 316.380 1 -total"," 27.82% 88.024 1 Template:Reflist"," 23.12% 73.162 2 Template:Cite_web"," 22.67% 71.735 1 Template:Commons_category"," 18.81% 59.497 1 Template:Citation_needed"," 17.41% 55.085 1 Template:Fix"," 11.98% 37.903 2 Template:Category_handler"," 11.22% 35.513 1 Template:Use_mdy_dates"," 10.59% 33.489 1 Template:Google_Inc."," 10.13% 32.049 4 Template:Navbox"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.118","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":4311027,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1263","timestamp":"20190106163325","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});});{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"Article","name":"ZygoteBody","url":"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZygoteBody","sameAs":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q170122","mainEntity":"http://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q170122","author":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Contributors to Wikimedia projects"},"publisher":{"@type":"Organization","name":"Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.","logo":{"@type":"ImageObject","url":"https://www.wikimedia.org/static/images/wmf-hor-googpub.png"}},"datePublished":"2010-12-18T16:47:35Z","dateModified":"2018-07-25T11:44:07Z","headline":"web application 3D of the human body"}(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":101,"wgHostname":"mw1274"});});

