Japanese archipelago
Japanese archipelago
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 Japanese archipelago shown in dark green | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 37°30′52″N 137°42′44″E / 37.514444°N 137.712222°E / 37.514444; 137.712222Coordinates: 37°30′52″N 137°42′44″E / 37.514444°N 137.712222°E / 37.514444; 137.712222 |
| Administration | |
Japan | |
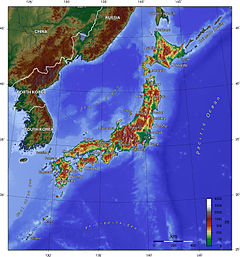
Topographic map of Japan

Satellite image of Japan
The Japanese archipelago (日本列島, Nihon Rettō) is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan. It extends over 3,000 km (1,900 mi)[1] from the Sea of Okhotsk northeast to the Philippine Sea south along the northeastern coast of the Eurasia continent. It consists of islands from the Sakhalin island arc, the Northeastern Japan arc to the Ryukyu islands and the Nanpō Islands.
The term Home Islands was used at the end of World War II to define the area of Japan to which its sovereignty and the constitutional rule of the Emperor would be restricted.[citation needed] The term is also commonly used today to distinguish the archipelago from Japan's colonies and other territories in the first half of the 20th century.[2]
Contents
1 Palaeogeography
2 Geography
2.1 Islands and prefectures
3 See also
4 References
Palaeogeography[edit]
.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery{display:table}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-default{background:transparent;margin-top:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-center{margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-left{float:left}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-right{float:right}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-none{float:none}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-collapsible{width:100%}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .title{display:table-row}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .title>div{display:table-cell;text-align:center;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .main{display:table-row}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .main>div{display:table-cell}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .caption{display:table-row;vertical-align:top}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .caption>div{display:table-cell;display:block;font-size:94%;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footer{display:table-row}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footer>div{display:table-cell;text-align:right;font-size:80%;line-height:1em}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox .thumb img{background:none}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .bordered-images img{border:solid #eee 1px}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .whitebg img{background:#fff!important}.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox div{background:#fff!important}

Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Early Miocene (23-18 Ma)
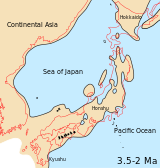
Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene (3.5-2 Ma)
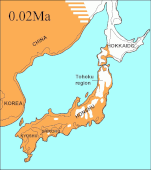
Japanese archipelago at the Last Glacial Maximum about 20,000 years ago, thin black line indicates present-day shorelines
Vegetated land
Unvegetated land
Ocean
Geography[edit]
The archipelago consists of 6,852 islands[3] (here defined as land more than 100 m in circumference), of which 430 are inhabited.[4] The four main islands, from north to south, are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu; Honshu is the largest and referred to as the Japanese mainland.[5]
The current Japanese archipelago topography is:
Sakhalin, Hokkaido, Honshu, Japan island arc composed of Shikoku and its surrounding islands;
Kyushu, Ryukyu arc composed of Nansei Islands and other surrounding islands;- Eastern part of Hokkaido (part of the Kuril arc);
Nanpō Islands, Izu Peninsula (part of Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc).
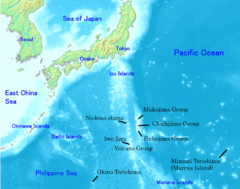
The Nanpō Islands administered by Tokyo Metropolis.

The Ryukyu Islands administered by Kagoshima Prefecture and Okinawa Prefecture.
Islands and prefectures[edit]
Hokkaido – The second largest island of Japan, and the largest and northernmost prefecture, which consists of 14 subprefectures.
 Hokkaido
Hokkaido
- Hidaka Subprefecture
- Hiyama Subprefecture
- Iburi Subprefecture
- Ishikari Subprefecture
- Kamikawa Subprefecture
- Kushiro Subprefecture
- Nemuro Subprefecture
- Okhotsk Subprefecture
- Oshima Subprefecture
- Rumoi Subprefecture
- Shiribeshi Subprefecture
- Sorachi Subprefecture
- Sōya Subprefecture
- Tokachi Subprefecture
Honshu – The largest and the most populated island of Japan, which consists of five regions.
Tōhoku region consists of six prefectures.
 Akita Prefecture
Akita Prefecture
 Aomori Prefecture
Aomori Prefecture
 Fukushima Prefecture
Fukushima Prefecture
 Iwate Prefecture
Iwate Prefecture
 Miyagi Prefecture
Miyagi Prefecture
 Yamagata Prefecture
Yamagata Prefecture
Kantō region consists of seven prefectures, including the capital of Japan which is the Tokyo Metropolis.
 Chiba Prefecture
Chiba Prefecture
 Gunma Prefecture
Gunma Prefecture
 Ibaraki Prefecture
Ibaraki Prefecture
 Kanagawa Prefecture
Kanagawa Prefecture
 Saitama Prefecture
Saitama Prefecture
 Tochigi Prefecture
Tochigi Prefecture
 Tokyo
Tokyo
Chūbu region consists of nine prefectures.
 Aichi Prefecture
Aichi Prefecture
 Fukui Prefecture
Fukui Prefecture
 Gifu Prefecture
Gifu Prefecture
 Ishikawa Prefecture
Ishikawa Prefecture
 Nagano Prefecture
Nagano Prefecture
 Niigata Prefecture
Niigata Prefecture
 Shizuoka Prefecture
Shizuoka Prefecture
 Toyama Prefecture
Toyama Prefecture
 Yamanashi Prefecture
Yamanashi Prefecture
Kansai region consists of seven prefectures.
 Hyōgo Prefecture
Hyōgo Prefecture
 Kyoto Prefecture
Kyoto Prefecture
 Mie Prefecture
Mie Prefecture
 Nara Prefecture
Nara Prefecture
 Osaka Prefecture
Osaka Prefecture
 Shiga Prefecture
Shiga Prefecture
 Wakayama Prefecture
Wakayama Prefecture
Chūgoku region consists of five prefectures.
 Hiroshima Prefecture
Hiroshima Prefecture
 Okayama Prefecture
Okayama Prefecture
 Shimane Prefecture
Shimane Prefecture
 Tottori Prefecture
Tottori Prefecture
 Yamaguchi Prefecture
Yamaguchi Prefecture
Shikoku – The smallest and the least populated island of the archipelago, which consists of four prefectures.
 Ehime Prefecture
Ehime Prefecture
 Kagawa Prefecture
Kagawa Prefecture
 Kōchi Prefecture
Kōchi Prefecture
 Tokushima Prefecture
Tokushima Prefecture
Kyushu – The third largest island of the archipelago, which consists of eight prefectures, including the Okinawa Islands in the Ryukyu island arc.
 Fukuoka Prefecture
Fukuoka Prefecture
 Kagoshima Prefecture
Kagoshima Prefecture
 Kumamoto Prefecture
Kumamoto Prefecture
 Miyazaki Prefecture
Miyazaki Prefecture
 Nagasaki Prefecture
Nagasaki Prefecture
 Ōita Prefecture
Ōita Prefecture
 Saga Prefecture
Saga Prefecture
 Okinawa Prefecture
Okinawa Prefecture
Sakhalin – Previously known and administered by the Empire of Japan as Karafuto Prefecture and a part of the Russian Federation, is sometimes considered to be geographically part of the Japanese archipelago, although Japan renounced its claim to the island in the 20th century.[6]
 Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast
See also[edit]
- Mainland Japan
- Japan in the Paleolithic
- List of islands of Japan
- Extreme points of Japan
References[edit]
^ "Water Supply in Japan". Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Archived from the original (website) on January 26, 2018. Retrieved 26 September 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Milton W. Meyer, Japan: A Concise History, 4th ed. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield, 2012,
ISBN 9780742541184, p. 2.
^ "離島とは(島の基礎知識)". Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. Archived from the original (website) on November 13, 2007. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
^ "Islands in Abundance", Look Japan Volume 43, Issues 493–504, p. 37.
^ "Japanese Archipelago", TheFreeDictionary.com, retrieved 24 June 2013.
^ "The Chautauquan", Volume 42, p. 6.
Categories:
- Japanese archipelago
- Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean
- Archipelagoes of Japan
- Geography of Japan
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"0.712","walltime":"1.110","ppvisitednodes":{"value":5892,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":114788,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":21286,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":14,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":20,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":14286,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":1,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 877.885 1 -total"," 29.92% 262.650 48 Template:Flagcountry"," 18.23% 160.002 1 Template:Infobox_islands"," 13.78% 120.956 1 Template:Reflist"," 13.46% 118.187 1 Template:Infobox"," 9.72% 85.354 1 Template:Japan_topics"," 9.30% 81.609 7 Template:Navbox"," 9.23% 80.991 1 Template:Country_topics"," 8.86% 77.812 2 Template:Cite_web"," 7.49% 65.720 1 Template:Refimprove"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"0.236","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":5998808,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1275","timestamp":"20190104041908","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":1234,"wgHostname":"mw1275"});});





