Shia Islam
Shia Islam
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} Part of a series on Shia Islam |
|---|
 |
Beliefs and practices
|
Holy days
|
History
|
Branches of Shi‘i Islam
|
Ahl al-Kisa
|
Holy women
|
Part of a series on Islam Aqidah |
|---|
 |
Five Pillars of Islam
|
Sunni Six articles of belief
Sunni theological traditions
|
Shi'a Twelver1
Seven pillars of Ismailism2
Other Shia concepts of Aqidah
|
Other schools of theology
|
Including: 1Alawites & Qizilbash 2Sevener-Qarmatians, Assassins & Druzes 3Ajardi, Azariqa, Bayhasiyya, Najdat & Sūfrī 4Nūkkārī; 5Bahshamiyya & Ikhshîdiyya 6Alevism, Bektashi Order & Qalandariyya |
| Part of a series on |
| Islam |
|---|
 |
Beliefs
|
Practices
|
Texts and laws
|
History
|
Culture and society
|
Related topics
|
|
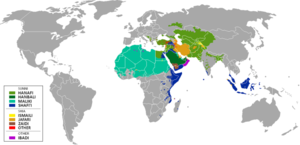
Shia (/ˈʃiːə/; Arabic: شيعة Shīʿah, from Shīʿatu ʿAlī, "adherent of Ali"), also transliterated Shiah and Shiʿah, is a branch of Islam which holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor and the Imam (leader) after him,[1] most notably at the event of Ghadir Khumm but was prevented caliphate as a result of Saqifah incident. This view primarily contrasts with that of Sunni Islam, whose adherents believe that Muhammad did not appoint a successor and consider Abu Bakr who they claim was appointed Caliph through a Shura, i.e. community consensus in Saqifa, to be the first rightful Caliph after the Prophet.[2]
As an offshoot of Islamic orthodoxy, this sectarian group began as a political boycott.
Unlike the first three Rashidun caliphs, Ali was from the same clan as Muhammad, Banu Hashim.[3]
Adherents of Shia Islam are called Shias of Ali, Shias or the Shi'a as a collective or Shi'i or Shi'ite individually.[4] Shia Islam is the second largest branch of Islam: in 2009, Shia Muslims constituted 10-20%[5] of the world's Muslim population.[6]Twelver Shia (Ithnā'ashariyyah) is the largest branch of Shia Islam,[7] with 2012 estimates saying that 85% of Shias were Twelvers.[8]

Ali ibn Abi Talib
Shia Islam is based on the Quran and the message of Muhammad attested in hadith, and on hadith taught by their Imams.[9][10] Shia consider Ali to have been divinely appointed as the successor to Muhammad, and as the first Imam. The Shia also extend this Imammah doctrine to Muhammad's family, the Ahl al-Bayt ("the people/family of the House"),[11] and some individuals among his descendants, known as Imams, who they believe possess special spiritual and political authority over the community, infallibility and other divinely ordained traits.[12] Although there are many Shia subsects, modern Shia Islam has been divided into three main groupings: Twelvers, Ismailis and Zaidis, with Twelver Shia being the largest and most influential group among Shia.[13][14][15]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 Terminology
3 Beliefs
3.1 Imamate
3.1.1 Succession of Ali
3.1.1.1 The event of Dhul Asheera
3.1.1.2 The event of Ghadir Khumm
3.1.2 Ali's caliphate
3.1.3 Hasan ibn Ali
3.1.4 Husayn
3.1.5 Imamate of the Ahl al-Bayt
3.1.6 Imam of the time, last Imam of the Shia
4 Theology
5 Hadith
6 Profession of faith
7 Infallibility
8 Occultation
9 Inheritance
10 History
11 North Africa
12 Iran and Caucasus
13 Arabian Peninsula
13.1 Bahrain
13.2 Yemen
14 Europe
15 Syria and Iraq
16 Asia Minor (Modern Turkey)
17 India
18 South-East Asia
19 East Africa
19.1 Fatimid caliphate
19.2 Safavids
20 Community
20.1 Demographics
20.1.1 Significant populations worldwide
20.2 Persecution
20.3 Holidays
20.4 Holy sites
21 Branches
21.1 Twelver
21.1.1 Doctrine
21.1.2 Books
21.1.3 The Twelve Imams
21.1.4 Jurisprudence
21.2 Zaidi ("Fiver")
21.2.1 Doctrine
21.2.2 Jurisprudence
21.2.3 Timeline
21.3 Ismaili
21.3.1 Ismaili imams
21.3.2 Pillars
21.3.3 Contemporary leadership
22 Other doctrines
22.1 Doctrine about necessity of acquiring knowledge
22.2 Doctrine concerning Du'a
23 See also
24 References
24.1 Bibliography
25 Further reading
26 External links
Etymology[edit]
The word Shia (Arabic: شيعة shīʻah /ˈʃiːʕa/) means follower[16] and is the short form of the historic phrase shīʻatu ʻAlī (شيعة علي /ˈʃiːʕatu ˈʕaliː/), meaning "followers of Ali", "faction of Ali", or "party of Ali".[17]Shi'a and Shiism are forms used in English, while Shi'ite or Shiite, as well as Shia, refer to its adherents.
Terminology[edit]
The term for the first time was used at the time of Muhammad.[18] At present, the word refers to the Muslims who believe that the leadership of the community after Muhammad belongs to Ali and his successors. Nawbakhti states that the term Shia refers to a group of Muslims that at the time of Muhammad and after him regarded Ali as the Imam and Caliph.[19]Al-Shahrastani expresses that the term Shia refers to those who believe that Ali is designated as the Heir, Imam and caliph by Muhammad[20] and also Ali's authority never goes out of his descendants.[21] For the Shia, this conviction is implicit in the Quran and history of Islam. Shia scholars emphasize that the notion of authority is linked to the family of the prophets as the verses 3:33,34 shows: "Indeed, Allah chose Adam and Noah and the family of Abraham and the family of 'Imran over the worlds – (33) Descendants, some of them from others. And Allah is Hearing and Knowing. (34)"[22] Shia search for the true meaning of the revelation to get the purpose of the life blood and the human destiny.[23]
Beliefs[edit]
Imamate[edit]
Succession of Ali[edit]
Shia Muslims believe that just as a prophet is appointed by God alone, only God has the prerogative to appoint the successor to his prophet. They believe God chose Ali to be Muhammad's successor, infallible, the first caliph (khalifah, head of state) of Islam. The Shias believe that Muhammad designated Ali as his successor by God's command (Eid Al Ghadir).[24][25]
Ali was Muhammad's first-cousin and closest living male relative as well as his son-in-law, having married Muhammad's daughter Fatimah.[26][27]
The event of Dhul Asheera[edit]
Muhammad invited people to Islam in secret for three years before he started inviting them publicly. In the fourth year of Islam, when Muhammad was commanded to invite his closer relatives to come to Islam[28] he gathered the Banu Hashim clan in a ceremony. At the banquet, he was about to invite them to Islam when Abu Lahab interrupted him, after which everyone left the banquet. The Prophet ordered Ali to invite the 40 people again. The second time, Muhammad announced Islam to them and invited them to join.[29] He said to them,
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
I offer thanks to Allah for His mercies. I praise Allah, and I seek His guidance. I believe in Him and I put my trust in Him. I bear witness that there is no god except Allah; He has no partners; and I am His messenger. Allah has commanded me to invite you to His religion by saying: And warn thy nearest kinsfolk. I, therefore, warn you, and call upon you to testify that there is no god but Allah, and that I am His messenger. O ye sons of Abdul Muttalib, no one ever came to you before with anything better than what I have brought to you. By accepting it, your welfare will be assured in this world and in the Hereafter. Who among you will support me in carrying out this momentous duty? Who will share the burden of this work with me? Who will respond to my call? Who will become my vicegerent, my deputy and my wazir?[30]
Ali was the only one to answer Muhammad's call. Muhammad told him to sit down, saying, "Wait! Perhaps someone older than you might respond to my call." Muhammad then asked the members of Banu Hashim a second time. Once again, Ali was the only one to respond, and again, Muhammad told him to wait. Muhammad then asked the members of Banu Hashim a third time. Ali was still the only volunteer. This time, Ali's offer was accepted by Muhammad. Muhammad "drew [Ali] close, pressed him to his heart, and said to the assembly: 'This is my wazir, my successor and my vicegerent. Listen to him and obey his commands.'"[31] In another narration, when Muhammad accepted Ali's eager offer, Muhammad "threw up his arms around the generous youth, and pressed him to his bosom" and said, "Behold my brother, my vizir, my vicegerent...Let all listen to his words, and obey him."[32]Sir Richard Burton writes about the banquet in his 1898 book, saying, "It won for [Muhammad] a proselyte worth a thousand sabers in the person of Ali, son of Abu Talib."[33]
The event of Ghadir Khumm[edit]
The event of Ghadir Khumm is an event that took place in March 632. While returning from the Hajj pilgrimage, the Islamic prophet Muhammad gathered all the Muslims who were with him and gave a long sermon. This sermon included Muhammad's declaration that "to whomsoever I am Mawla, Ali is also their Mawla." After the sermon, Muhammad instructed everyone to pledge allegiance to Ali. Shia Muslims believe this event to be the official appointment of Ali as Muhammad's successor.[34]
A portion of the sermon Muhammad delivered is as follows:
Oh people! Reflect on the Quran and comprehend its verses. Look into its clear verses and do not follow its ambiguous parts, for by Allah, none shall be able to explain to you its warnings and its mysteries, nor shall anyone clarify its interpretation, other than the one that I have grasped his hand, brought up beside myself, [and lifted his arm,] the one about whom I inform you that whomever I am his master (Mawla[a]), then Ali is his master (Mawla); and he is Ali Ibn Abi Talib, my brother, the executor of my will (Wasiyyi), whose appointment as your guardian and leader has been sent down to me from Allah, the mighty and the majestic.
— Muhammad, from The Farewell Sermon[37]
^ The word mawla has many meanings in Arabic; however, Shias argue that the context of the sermon makes the meaning of "mawla" as "leader" in this context clear.[35] Further, "mawla" was not the only word that Muhammad used in this sermon to describe Ali; he also used the words "wali," "Imam," and "khalifa." All of this together cements the leadership of Ali as described in the sermon delivered by Muhammad. Further, according to Shias, the combination of these words proves that Ali's leadership, as described by Muhammad in this sermon, is both a religious leadership as well as a political leadership, as the meanings of these words indicate.[36]
After the conclusion of Muhammad's sermon, the Muslims were commanded to pledge their allegiance to Ali. Umar was reportedly the first to give the oath of allegiance to Ali.
Shia Muslims believe this to be Muhammad's appointment of Ali as his successor.
Ali's caliphate[edit]

The Investiture of Ali at Ghadir Khumm (MS Arab 161, fol. 162r, AD 1309/8 Ilkhanid manuscript illustration)
When Muhammad died in 632 CE, Ali and Muhammad's closest relatives made the funeral arrangements. While they were preparing his body, Abu Bakr, Umar, and Abu Ubaidah ibn al Jarrah met with the leaders of Medina and elected Abu Bakr as caliph. Ali did not accept the caliphate of Abu Bakr and refused to pledge allegiance to him. This is indicated in both Sunni and Shia sahih and authentic Hadith.
Ibn Qutaybah, a 9th-century Sunni Islamic scholar narrates of Ali:
I am the servant of God and the brother of the Messenger of God. I am thus more worthy of this office than you. I shall not give allegiance to you [Abu Bakr & Umar] when it is more proper for you to give bay’ah to me. You have seized this office from the Ansar using your tribal relationship to the Prophet as an argument against them. Would you then seize this office from us, the ahl al-bayt by force? Did you not claim before the Ansar that you were more worthy than they of the caliphate because Muhammad came from among you (but Muhammad was never from AbuBakr family) – and thus they gave you leadership and surrendered command? I now contend against you with the same argument…It is we who are more worthy of the Messenger of God, living or dead. Give us our due right if you truly have faith in God, or else bear the charge of wilfully doing wrong... Umar, I will not yield to your commands: I shall not pledge loyalty to him.' Ultimately Abu Bakr said, "O 'Ali! If you do not desire to give your bay'ah, I am not going to force you for the same.
Ali's wife, and daughter of Muhammad, Fatimah, refused to pledge allegiance to Abu Bakr and remained angry with him until she died due to the issues of Fadak and her inheritance from her father and the situation of Umar at Fatimah's house. This is stated in sahih Sunni Hadith, Sahih Bukhari and Sahih Muslim. Fatimah did not at all pledge allegiance or acknowledge or accept the caliphate of Abu Bakr.[38] Almost all of Banu Hashim, Muhammad's clan and many of the sahaba, had supported Ali's cause after the demise of the prophet whilst others supported Abu Bakr.[39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46][47]
It was not until the murder of the third caliph, Uthman, in 657 CE that the Muslims in Medina in desperation invited Ali to become the fourth caliph as the last source,[26] and he established his capital in Kufah in present-day Iraq.[17]
Ali's rule over the early Muslim community was often contested, and wars were waged against him. As a result, he had to struggle to maintain his power against the groups who betrayed him after giving allegiance to his succession, or those who wished to take his position. This dispute eventually led to the First Fitna, which was the first major civil war within the Islamic Caliphate. The Fitna began as a series of revolts fought against Ali ibn Abi Talib, caused by the assassination of his political predecessor, Uthman ibn Affan. While the rebels who accused Uthman of prejudice[clarification needed] affirmed Ali's khilafa (caliph-hood), they later turned against him and fought him.[26] Ali ruled from 656 CE to 661 CE,[26] when he was assassinated[27] while prostrating in prayer (sujud). Ali's main rival Muawiyah then claimed the caliphate.[48]
Hasan ibn Ali[edit]
Upon the death of Ali, his elder son Hasan became leader of the Muslims of Kufa, and after a series of skirmishes between the Kufa Muslims and the army of Muawiyah, Hasan agreed to cede the caliphate to Muawiyah and maintain peace among Muslims upon certain conditions:[49][50]
- The enforced public cursing of Ali, e.g. during prayers, should be abandoned
- Muawiyah should not use tax money for his own private needs
- There should be peace, and followers of Hasan should be given security and their rights
- Muawiyah will never adopt the title of Amir al-Mu'minin
- Muawiyah will not nominate any successor
Hasan then retired to Medina, where in 670 CE he was poisoned by his wife Ja'da bint al-Ash'ath ibn Qays, after being secretly contacted by Muawiyah who wished to pass the caliphate to his own son Yazid and saw Hasan as an obstacle.
Husayn[edit]

The Imam Hussein Shrine in Karbala, Iraq is a holy site for Shia Muslims.

Battle of Karbala, Brooklyn Museum
Husayn, Ali's younger son and brother to Hasan, initially resisted calls to lead the Muslims against Muawiyah and reclaim the caliphate. In 680 CE, Muawiyah died and passed the caliphate to his son Yazid, and breaking the treaty with Hasan ibn Ali. Yazid asked Husayn to swear allegiance (bay'ah) to him. Ali's faction, having expected the caliphate to return to Ali's line upon Muawiyah's death, saw this as a betrayal of the peace treaty and so Husayn rejected this request for allegiance. There was a groundswell of support in Kufa for Husayn to return there and take his position as caliph and imam, so Husayn collected his family and followers in Medina and set off for Kufa. En route to Kufa, he was blocked by an army of Yazid's men (which included people from Kufa) near Karbala (modern Iraq), and Husayn and approximately 72 of his family and followers were killed in the Battle of Karbala.
The Shias regard Husayn as a martyr (shahid), and count him as an Imam from the Ahl al-Bayt. They view Husayn as the defender of Islam from annihilation at the hands of Yazid I. Husayn is the last imam following Ali whom all Shiah sub-branches mutually recognize.[51] The Battle of Karbala is often cited as the definitive break between the Shiah and Sunni sects of Islam, and is commemorated each year by Shiah Muslims on the Day of Ashura.
Imamate of the Ahl al-Bayt[edit]

Zulfiqar with and without the shield. The Fatimid depiction of Ali's sword as carved on the Gates of Old Cairo, namely Bab al-Nasr shown below. Two swords were captured from the temple of the pagan polytheist god Manāt during the Raid of Sa'd ibn Zaid al-Ashhali. Muhammad gave them to Ali, saying that one of them was Zulfiqar, which became the famous sword of Ali and a later symbol of Shiism.[52]

Ali's Sword and shield depiction at Bab al Nasr gate wall, Cairo
Most of the early Shia differed only marginally from mainstream Sunnis in their views on political leadership, but it is possible in this sect to see a refinement of Shia doctrine. Early Sunnis traditionally held that the political leader must come from the tribe of Muhammad—namely, the Quraysh tribe. The Zaydis narrowed the political claims of Ali's supporters, claiming that not just any descendant of Ali would be eligible to lead the Muslim community (ummah) but only those males directly descended from Muhammad through the union of Ali and Fatimah. But during the Abbasid revolts, other Shia, who came to be known as Imamiyyah (followers of the Imams), followed the theological school of Imam Ja'far al-Sadiq, himself the great great grandson of Muhammad's son-in-law Imam Ali. They asserted a more exalted religious role for Imams and insisted that, at any given time, whether in power or not, a single male descendant of Ali and Fatimah was the divinely appointed Imam and the sole authority, in his time, on all matters of faith and law. To those Shia, love of the Imams and of their persecuted cause became as important as belief in God's oneness and the mission of Muhammad.[citation needed]
Later most of the Shia, including Twelver and Ismaili, became Imamis. Imami Shia believe that Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad.[citation needed] Imams are human individuals who not only rule over the community with justice, but also are able to keep and interpret the divine law and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the imams are a guide and model for the community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and must be chosen by divine decree, or nass, through Muhammad.[53][54]
According to this view, there is always an Imam of the Age, who is the divinely appointed authority on all matters of faith and law in the Muslim community. Ali was the first imam of this line, the rightful successor to Muhammad, followed by male descendants of Muhammad through his daughter Fatimah.[citation needed]
This difference between following either the Ahl al-Bayt (Muhammad's family and descendants) or Caliph Abu Bakr has shaped Shia and non-Shia views on some of the Quranic verses, the hadith (narrations from Muhammad) and other areas of Islam. For instance, the collection of hadith venerated by Shia Muslims is centered on narrations by members of the Ahl al-Bayt and their supporters, while some hadith by narrators not belonging to or supporting the Ahl al-Bayt are not included. Those of Abu Hurairah, for example, Ibn Asakir in his Ta'rikh Kabir and Muttaqi in his Kanzu'l-Umma report that Caliph Umar lashed him, rebuked him and forbade him to narrate hadith from Muhammad. Umar said: "Because you narrate hadith in large numbers from the Holy Prophet, you are fit only for attributing lies to him. (That is, one expects a wicked man like you to utter only lies about the Holy Prophet.) So you must stop narrating hadith from the Prophet; otherwise, I will send you to the land of Dus." (A clan in Yemen, to which Abu Huraira belonged.) According to Sunnis, Ali was the fourth successor to Abu Bakr, while the Shia maintain that Ali was the first divinely sanctioned "Imam", or successor of Muhammad. The seminal event in Shia history is the martyrdom in 680 CE at the Battle of Karbala of Ali's son Hussein ibn Ali, who led a non-allegiance movement against the defiant caliph (71 of Hussein's followers were killed as well). Hussein came to symbolize resistance to tyranny.
It is believed in Twelver and Ismaili Shia Islam that 'aql, divine wisdom, was the source of the souls of the prophets and imams and gave them esoteric knowledge called ḥikmah and that their sufferings were a means of divine grace to their devotees.[55][56] Although the imam was not the recipient of a divine revelation, he had a close relationship with God, through which God guides him, and the imam, in turn, guides the people. Imamate, or belief in the divine guide, is a fundamental belief in the Twelver and Ismaili Shia branches and is based on the concept that God would not leave humanity without access to divine guidance.[57]
Imam of the time, last Imam of the Shia[edit]
The Mahdi is the prophesied redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine or nineteen years (according to differing interpretations) before the Day of Judgment and will rid the world of evil. According to Islamic tradition, the Mahdi's tenure will coincide with the Second Coming of Jesus Christ (Isa), who is to assist the Mahdi against the Masih ad-Dajjal (literally, the "false Messiah" or Antichrist). Jesus, who is considered the Masih (Messiah) in Islam, will descend at the point of a white arcade, east of Damascus, dressed in yellow robes with his head anointed. He will then join the Mahdi in his war against the Dajjal, where Jesus will slay Dajjal and unite mankind.
Theology[edit]
The Shia Islamic faith is vast and inclusive of many different groups.[17] Shia theological beliefs and religious practises, such as prayers, slightly differ from the Sunnis'. While all Muslims pray five times daily, Shias have the option of combining Dhuhr with Asr and Maghrib with Isha', as there are three distinct times mentioned in the Quran. The Sunnis tend to combine only under certain circumstances.[58][59] Shia Islam embodies a completely independent system of religious interpretation and political authority in the Muslim world.[60][61] The original Shia identity referred to the followers of Imam Ali,[62] and Shia theology was formulated in the 2nd century AH, or after Hijra (8th century CE).[63] The first Shia governments and societies were established by the end of the 3rd century AH/9th century CE. The 4th century AH /10th century CE has been referred to by Louis Massignon as "the Shiite Ismaili century in the history of Islam".[64]
Hadith[edit]
The Shia believe that the status of Ali is supported by numerous hadith, including the Hadith of the pond of Khumm, Hadith of the two weighty things, Hadith of the pen and paper, Hadith of the invitation of the close families, and Hadith of the Twelve Successors. In particular, the Hadith of the Cloak is often quoted to illustrate Muhammad's feeling towards Ali and his family by both Sunni and Shia scholars. Shias prefer hadith attributed to the Ahl al-Bayt and close associates, and have their own separate collection of hadiths.[65][66]
Profession of faith[edit]
This section does not cite any sources. (February 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

Kalema at Qibla of the Mosque of Ibn Tulun in Cairo, Egypt with phrase "Ali-un-Waliullah"
The Shia version of the Shahada, the Islamic profession of faith, differs from that of the Sunni. The Sunni Shahada states There is no god except Allah, Muhammad is the messenger of Allah, but to this the Shia append Ali is the Wali (custodian) of God, علي ولي الله. This phrase embodies the Shia emphasis on the inheritance of authority through Muhammad's lineage. The three clauses of the Shia Shahada thus address tawhid (the unity of God), nubuwwah (the prophethood of Muhammad), and imamah (imamate, the leadership of the faith).
The basis of Ali as the "wali" is taken from a specific verse of the quran
[67]. A more detailed discussion of this verse is available[68].
Infallibility[edit]

Ali is credited as the first male to convert to Islam.
Ismah is the concept of infallibility or "divinely bestowed freedom from error and sin" in Islam.[69] Muslims believe that Muhammad and other prophets in Islam possessed ismah. Twelver and Ismaili Shia Muslims also attribute the quality to Imams as well as to Fatimah, daughter of Muhammad, in contrast to the Zaidi, who do not attribute 'ismah to the Imams.[70] Though initially beginning as a political movement, infallibility and sinlessness of the imams later evolved as a distinct belief of (non-Zaidi) Shiism.[citation needed]
According to Shia theologians, infallibility is considered a rational necessary precondition for spiritual and religious guidance. They argue that since God has commanded absolute obedience from these figures they must only order that which is right. The state of infallibility is based on the Shia interpretation of the verse of purification.[71][72] Thus, they are the most pure ones, the only immaculate ones preserved from, and immune to, all uncleanness.[73] It does not mean that supernatural powers prevent them from committing a sin, but due to the fact that they have absolute belief in God, they refrain from doing anything that is a sin.[74]
They also have a complete knowledge of God's will. They are in possession of all knowledge brought by the angels to the prophets (nabi) and the messengers (rasul). Their knowledge encompasses the totality of all times. They thus act without fault in religious matters.[75] Shias regard Ali as the successor of Muhammad not only ruling over the community in justice, but also interpreting Islamic practices and its esoteric meaning. Hence he was regarded as being free from error and sin (infallible), and appointed by God by divine decree (nass) to be the first Imam.[76] Ali is known as "perfect man" (al-insan al-kamil) similar to Muhammad, according to Shia viewpoint.[77]
Occultation[edit]
The Occultation is a belief in some forms of Shia Islam that a messianic figure, a hidden imam known as the Mahdi, will one day return and fill the world with justice. According to the Twelver Shia, the main goal of the Mahdi will be to establish an Islamic state and to apply Islamic laws that were revealed to Muhammad.[78]
Some Shia, such as the Zaidi and Nizari Ismaili, do not believe in the idea of the Occultation. The groups which do believe in it differ as to which lineage of the Imamate is valid, and therefore which individual has gone into occultation. They believe there are many signs that will indicate the time of his return.
Twelver Shia Muslims believe that the Mahdi (the twelfth imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi) is already on Earth, is in occultation and will return at the end of time. Fatimid/ Bohra/ Dawoodi Bohra believe the same but for their 21st Tayyib, whereas Sunnis believe the future Mahdi has not yet arrived on Earth.[79]
Inheritance[edit]
It is believed that the armaments and sacred items of all of the Prophets, including Muhammad, were handed down in succession to the Imams of Ahl al-Bayt. In Kitab al-Kafi, Ja'far al-Sadiq mentions that "with me are the arms of the Messenger of Allah. It is not disputable."[80].
Further, he claims that with him is the sword of the Messenger of Allah, his coat of arms, his Lamam (pennon) and his helmet. In addition, he mentions that with him is the flag of the Messenger of Allah, the victorious. With him is the Staff of Moses, the ring of Solomon, son of David, and the tray on which Moses used to offer his offerings. With him is the name that whenever the Messenger of Allah would place it between the Muslims and pagans no arrow from the pagans would reach the Muslims. With him is the similar object that angels brought.[80].
Al-Sadiq also narrates that the passing down of armaments is synonymous to receiving the Imamat (leadership), similar to how the Ark in the house of the Israelites signaled prophet-hood.[80].
Imam Ali al-Ridha narrates that wherever the armaments among us would go, knowledge would also follow and the armaments would never depart from those with knowledge (Imamat). [80]
History[edit]

Ghazan and his brother Öljaitü both were tolerant of sectarian differences within the boundaries of Islam, in contrast to the traditions of Genghis Khan.
Historians dispute the origin of Shia Islam, with many Western scholars positing that Shiism began as a political faction rather than a truly religious movement.[81][82] Other scholars disagree, considering this concept of religious-political separation to be an anachronistic application of a Western concept.[83]
Following the Battle of Karbala (680 AD), as various Shia-affiliated groups diffused in the emerging Islamic world, several nations arose based on a Shia leadership or population.
Idrisids (788 to 985 CE): a Zaydi dynasty in what is now Morocco
Uqaylids (990 to 1096 CE): a Shia Arab dynasty with several lines that ruled in various parts of Al-Jazira, northern Syria and Iraq.
Buyids (934–1055 CE): at its peak consisted of large portions of modern Iraq and Iran.
Ilkhanate (1256–1335): a Mongol khanate established in Persia in the 13th century, considered a part of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanate was based, originally, on Genghis Khan's campaigns in the Khwarezmid Empire in 1219–1224, and founded by Genghis's grandson, Hulagu, in territories which today comprise most of Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkey, and Pakistan. The Ilkhanate initially embraced many religions, but was particularly sympathetic to Buddhism and Christianity. Later Ilkhanate rulers, beginning with Ghazan in 1295, embraced Islam his brother Öljaitü promoted Shia Islam.[clarification needed]
Naubat Khan accepted Islam under the Guidance of Mughal General Bairam Khan's son Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana.
Bahmanis (1347–1527 CE): a Shia Muslim state of the Deccan in southern India and one of the great medieval Indian kingdoms.[84] Bahmanid Sultanate was the first independent Islamic Kingdom in South India.[85]
North Africa[edit]
Idrisid dynasty (780–985 CE) — Zaidi[86]
Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171 CE) — Ismaili
Banu Kanz (1004–1412 CE)[87]
Iran and Caucasus[edit]
Justanids (791–974 CE) — Zaidi
Alavids (864–929 CE) — Zaidi
Aishanids (912–961 CE)
Ziyarid dynasty (928–1043 CE)
Buyid dynasty (934–1062 CE) — Zaidi, later converted to Twelver[88]
Hasanwayhid (959–1015 CE)
Kakuyids (1008–1051 CE)
Nizari Ismaili state (1090–1256 CE) — Nizari
Sarbadars (1332–1386 CE) — Twelver[89]
Injuids (1335–1357 CE) — Twelver[89]
Marashiyan (1359–1582 CE)
Kara Koyunlu (1375–1468 CE)
Musha'sha'iyyah dynasty (1436–1729 CE) — Musha'sha'iyyah
Safavid dynasty (1501–1736 CE) — Twelver[90]
Baku Khanate (1753–1806 CE)
Erivan Khanate (1604–1828 CE)
Derbent Khanate (1747–1806 CE)
Ganja Khanate (1747–1804 CE)
Javad Khanate (1747-1805 CE)
Talysh Khanate (1747–1828 CE)
Nakhichevan Khanate (1747–1813 CE)
Karabakh Khanate (1747–1822 CE)
Zand dynasty (1750–1794 CE)
Qajar dynasty (1785–1925 CE)
Pahlavi dynasty (1925–1979 CE)
Arabian Peninsula[edit]
Bahrain[edit]
Qarmatians (900–1073 CE) — Qarmatians
Uyunid dynasty (1073-1253 CE) — Twelver[91]
Usfurids (1253–1320 CE) — Twelver[91]
Jarwanid dynasty (1305–1487 CE)[92] — Ismaili and Twelver[93]
Jabrids (15/16th century) — Twelver[94]
Yemen[edit]
Banu Ukhaidhir (865–1066 CE) — Zaidi
Rassids (893–1970 CE) — Zaidi
Sulaihid State (1047–1138 CE) — Ismaili[95]
Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1926–1970 AD) — Zaidi
Europe[edit]
Kalbids (948–1053 AD)
Hammudid dynasty (1016–1073 AD) — Zaidi[96]
Syria and Iraq[edit]
Hamdanid dynasty (890–1004 CE)
Bani Assad (961–1163 CE) (central and southern Iraq)
Numayrids (990–1081 CE) (eastern Syria and southeastern Turkey)
Marwanids (990–1085 CE)
Uqaylid Dynasty (990–1169 CE)
Mirdasids (1024–1080 CE)
Asia Minor (Modern Turkey)[edit]
Eretnids (1328–1381 CE)
Danishmends (1071–1178 CE)
Beylik of Erzincan (1379–1410 CE)
India[edit]
Bahmani Sultanate (1347–1527 CE)
Jaunpur Sultanate (1394–1479 CE)
Bidar Sultanate (1489–1619 CE)
Berar Sultanate (1490–1572 CE)
Ahmadnagar Sultanate (1490–1636 CE)
Qutb Shahi dynasty (1512–1687 CE)
Adil Shahi dynasty (1490–1686 CE)
Najm-i-Sani dynasty (1658–? CE)
Nawab of Rampur (1719–1949 CE)
Nawabs of Oudh (1722–1858 CE)
Nawabs of Bengal (1757–1880 CE)
Talpur dynasty (1783–1843 CE)[97]
Hunza (princely state) (1500s—1974 CE)
Nagar (princely state) (14th Century—1974 CE)
South-East Asia[edit]
Daya Pasai (1128–1285 CE).[98]
Bandar Kalibah[99]
Moira Malaya[100]
Kanto Kambar[101]
Robaromun[102]
East Africa[edit]
Kilwa Sultanate (957–1506 CE).[103]
Fatimid caliphate[edit]
Fatimids (909–1171 CE): Controlled much of North Africa, the Levant, parts of Arabia and Mecca and Medina. The group takes its name from Fatima, Muhammad's daughter, from whom they claim descent.- In 909 CE the Shiite military leader Abu Abdallah, overthrew the Sunni ruler in Northern Africa; which began the Fatimid regime.[104]
Safavids[edit]

One of Shah Ismail I of Safavid dynasty first actions, was the proclamation of the Twelver sect of Shia Islam to be the official religion of his newly formed state. Causing sectarian tensions in the Middle East when he destroyed the tombs of Abū Ḥanīfa and the Sufi Abdul Qadir Gilani in 1508.[105] In 1533, Ottomans, upon their conquest of Iraq, rebuilt various important Sunni shrines.[106]
A major turning point in Shia history was the Safavid dynasty (1501–1736) in Persia. This caused a number of changes in the Muslim world:
- The ending of the relative mutual tolerance between Sunnis and Shias that existed from the time of the Mongol conquests onwards and the resurgence of antagonism between the two groups.
- Initial dependence of Shiite clerics on the state followed by the emergence of an independent body of ulama capable of taking a political stand different from official policies.[107]
- The growth in importance of Iranian centers of religious learning and change from Twelver Shiism being a predominantly Arab phenomenon.[108]
- The growth of the Akhbari School which preached that only the Quran, hadith are to be bases for verdicts, rejecting the use of reasoning.
With the fall of the Safavids, the state in Persia – including the state system of courts with government-appointed judges (qadis) – became much weaker. This gave the Sharia courts of mujtahids an opportunity to fill the legal vacuum and enabled the ulama to assert their judicial authority. The Usuli School also increased in strength at this time.[109]

The declaration of Shiism as the state religion of the Safavid dynasty in Persia.
Monument commemorating the Battle of Chaldiran, where more than 7000 Muslims of Shia and Sunni sects were killed in battle.

Battle of Chaldiran, was a major sectarian crisis in the Middle East.
Community[edit]
Demographics[edit]

Islam by country Sunni Shias Ibadi
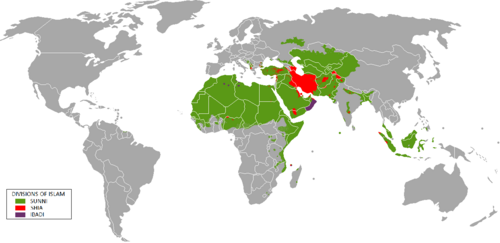
Distribution of Sunni and Shia branches of Islam
According to Shia Muslims, one of the lingering problems in estimating Shia population is that unless Shia form a significant minority in a Muslim country, the entire population is often listed as Sunni. The reverse, however, has not held true, which may contribute to imprecise estimates of the size of each sect. For example, the 1926 rise of the House of Saud in Arabia brought official discrimination against Shia.[110] Shiites are estimated to be 21–35% of the Muslim population in South Asia, although the total number is difficult to estimate due to that reason.[111]
It is variously estimated that 10–20%[112][113][114][115] of the world's Muslims are Shia. They may number up to 200 million as of 2009.[114]
The Shia majority countries are Iran, Iraq, Azerbaijan, and Bahrain.[116][117] They also form the plurality (the largest group, but not the majority) in Lebanon. Shias constitute 36.3% of entire local population and 38.6% of the local Muslim population of the Middle East.[118]
Shia Muslims constitute 27-35% of the population in Lebanon, and as per some estimates from 35%[116][119] to over 35–40% of the population in Yemen,[120] 30%–35% of the citizen population in Kuwait (no figures exist for the non-citizen population),[121][122] over 20% in Turkey,[114][123] 5–20% of the population in Pakistan,[124][114] and 10–19% of Afghanistan's population.[125][126]
Saudi Arabia hosts a number of distinct Shia communities, including the Twelver Baharna in the Eastern Province and Nakhawila of Medina, and the Ismaili Sulaymani and Zaidiyyah of Najran. Estimations put the number of Shiite citizens at 2–4 million, accounting for roughly 15% of the local population.[127][better source needed]
Significant Shia communities exist in the coastal regions of West Sumatra and Aceh in Indonesia (see Tabuik).[128] The Shia presence is negligible elsewhere in Southeast Asia, where Muslims are predominantly Shafi'i Sunnis.
A significant Shia minority is present in Nigeria, made up of modern-era converts to a Shia movement centered around Kano and Sokoto states.[114][115][129] Several African countries like Kenya,[130] South Africa,[131] Somalia,[132] etc. hold small minority populations of various Shia denominations, primarily descendants of immigrants from South Asia during the colonial period, such as the Khoja.[133]
Significant populations worldwide[edit]
Distribution of global Shia Muslim population among the continents
Asia (93.3%)
Africa (4.4%)
Europe (1.5%)
Americas (0.7%)
Australia (0.1%)
Figures indicated in the first three columns below are based on the October 2009 demographic study by the Pew Research Center report, Mapping the Global Muslim Population.[114][115]
| Country | Shia population[114][115] | Percent of Muslim population that is Shia[114][115] | Percent of global Shia population[114][115] | Minimum estimate/claim | Maximum estimate/claim |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Iran | 74,000,000 – 78,000,000 | 90–95 | 37–40 | 78,661,551[134][135] | |
Pakistan | 17,000,000 – 26,000,000 | 10–15 | 10–15 | 43,250,000[136] – 57,666,666[137][138] | |
India | 17,000,000 – 26,000,000 | 10–15 | 9–14 | 40,000,000[139] – 50,000,000.[140] | |
Iraq | 19,000,000 – 22,000,000 | 65–70 | 11–12 | ||
Yemen | 8,000,000 – 10,000,000 | 35–40 | ~5 | ||
Turkey | 7,000,000 – 11,000,000 | 10–15 | 4–6 | 22 million[134] | |
Azerbaijan | 5,000,000 – 7,000,000 | 65–75 | 3–4 | 8.16 million,[134] 85% of total population[141] | |
Afghanistan | 3,000,000 – 4,000,000 | 10–15 | ~2 | 6.1 million,[134] 15–19% of total population[125] | |
Syria | 3,000,000 – 4,000,000 | 15–20 | ~2 | ||
Saudi Arabia | 2,000,000 – 4,000,000 | 10–15 | 1–2 | ||
Nigeria | <4,000,000 | <5 | <2 | 22-25 million[142][not in citation given] | |
Bangladesh | 40,000 – 50,000 | <1 | <1 | 10,840,000[143] | |
Lebanon | 1,000,000 – 2,000,000 | 45–55 | <1 | Estimated, no official census.[144] 50–55%[145][146][147] | |
Tanzania | <2,000,000 | <10 | <1 | ||
Kuwait | 500,000 - 700,000 | 20-25 | <1 | 30%-35% of 1.2m Muslims (citizen only)[121][122] | |
Germany | 400,000 – 600,000 | 10–15 | <1 | ||
Bahrain | 400,000 – 500,000 | 65–70 | <1 | 100,000 (66%[148] of citizen population) | 200,000 (70%[149] of citizen population) |
Tajikistan | ~400,000 | ~7 | ~1 | ||
United Arab Emirates | 300,000 – 400,000 | 10 | <1 | ||
United States | 200,000 – 400,000 | 10–15 | <1 | ||
Oman | 100,000 – 300,000 | 5–10 | <1 | 948,750[150] | |
United Kingdom | 100,000 – 300,000 | 10–15 | <1 | ||
Qatar | ~100,000 | ~10 | <1 |
Persecution[edit]
The history of Sunni-Shia relations has often involved violence, dating back to the earliest development of the two competing sects.
At various times Shia groups have faced persecution.[151][152][153][154][155][156]
Militarily established and holding control over the Umayyad government, many Sunni rulers perceived the Shia as a threat – to both their political and their religious authority.[157] The Sunni rulers under the Umayyads sought to marginalize the Shia minority, and later the Abbasids turned on their Shia allies and imprisoned, persecuted, and killed them. The persecution of the Shia throughout history by Sunni co-religionists has often been characterized by brutal and genocidal acts. Comprising only about 10–15% of the entire Muslim population, the Shia remain a marginalized community to this day in many Sunni Arab dominant countries without the rights to practice their religion and organize.[158]
In 1514 the Ottoman sultan, Selim I, ordered the massacre of 40,000 Anatolian Shia.[159] According to Jalal Al-e-Ahmad, "Sultan Selim I carried things so far that he announced that the killing of one Shiite had as much otherworldly reward as killing 70 Christians."[160]
In 1801 the Al Saud-Wahhabi armies attacked and sacked Karbala, the Shia shrine in eastern Iraq that commemorates the death of Husayn.[161]
Under Saddam Hussein's regime, 1968 to 2003, in Iraq, Shia Muslims were heavily arrested, tortured and killed.[162]
In March 2011, the Malaysian government declared the Shia a "deviant" sect and banned them from promoting their faith to other Muslims, but left them free to practice it themselves privately.[163][164]
Holidays[edit]
Shia, celebrate the following annual holidays:
Eid ul-Fitr, which marks the end of fasting during the month of Ramadan
Eid al-Adha, which marks the end of the Hajj or pilgrimage to Mecca
The following days are some of the most important holidays observed by Shia Muslims:
Eid al-Ghadeer, which is the anniversary of the Ghadir Khum, the occasion when Muhammad announced Ali's Imamate before a multitude of Muslims.[165] Eid al-Ghadeer is held on the 18th of Dhu al-Hijjah.- The Mourning of Muharram and the Day of Ashura for Shia commemorates Husayn ibn Ali's martyrdom. Husayn was a grandson of Muhammad who was killed by Yazid ibn Muawiyah. Ashurah is a day of deep mourning which occurs on the 10th of Muharram.
Arba'een commemorates the suffering of the women and children of Husayn ibn Ali's household. After Husayn was killed, they were marched over the desert, from Karbala (central Iraq) to Shaam (Damascus, Syria). Many children (some of whom were direct descendants of Muhammad) died of thirst and exposure along the route. Arbaein occurs on the 20th of Safar, 40 days after Ashurah.
Mawlid, Muhammad's birth date. Unlike Sunni Muslims, who celebrate the 12th of Rabi' al-awwal as Muhammad's birthday or deathday (because they assert that his birth and death both occur in this week), Shia Muslims celebrate Muhammad's birthday on the 17th of the month, which coincides with the birth date of the sixth imam, Ja'far al-Saadiq.[166]Wahhabis do not celebrate Muhammad's birthday, believing that such celebrations constitute a bid‘ah.[167]
Fatimah's birthday on 20th of Jumada al-Thani. This day is also considered as the "'women and mothers' day"[168]
Ali's birthday on 13th of Rajab.
Mid-Sha'ban is the birth date of the 12th and final Twelver imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi. It is celebrated by Shia Muslims on the 15th of Sha'aban.
Laylat al-Qadr, anniversary of the night of the revelation of the Quran.
Eid al-Mubahila celebrates a meeting between the Ahl al-Bayt (household of Muhammad) and a Christian deputation from Najran. Al-Mubahila is held on the 24th of Dhu al-Hijjah.
Holy sites[edit]
The four holiest sites to Muslims are Mecca (Al-Haram Mosque), Medina (Al-Nabbawi Mosque), Jerusalem (Al-Aqsa Mosque), and Kufa (Kufa Mosque). In addition for Shias, the Imam Husayn Shrine, Al Abbas Mosque in Karbala, and Imam Ali Mosque in Najaf are also highly revered.
Other venerated sites include Wadi-us-Salaam cemetery in Najaf, Al-Baqi' cemetery in Medina, Imam Reza shrine in Mashhad, Kadhimiya Mosque in Kadhimiya, Al-Askari Mosque in Samarra, Sahla Mosque and Great Mosque of Kufa in Kufa and several other sites in the cities of Qom, Susa and Damascus.
Most of the Shia holy places in Saudi Arabia have been destroyed by the warriors of the Ikhwan, the most notable being the tombs of the Imams in the Al-Baqi' cemetery in 1925.[169] In 2006, a bomb destroyed the shrine of Al-Askari Mosque.[170]
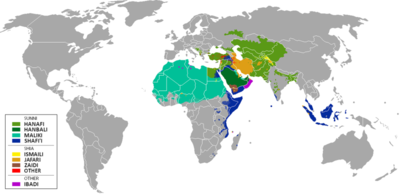
Branches[edit]
The Shia belief throughout its history split over the issue of the Imamate. The largest branch are the Twelvers, followed by the Zaidi and Ismaili. All three groups follow a different line of Imamate.
File:Imam chart.pdf
Twelver[edit]
Twelver Shia or the Ithnā'ashariyyah' is the largest branch of Shia Islam, and the term Shia Muslim often refers to the Twelvers by default. The term Twelver is derived from the doctrine of believing in twelve divinely ordained leaders, known as The Twelve Imams. Twelver Shia are also known as Imami or Ja'fari, originated from the name of the 6th Imam, Ja'far al-Sadiq, who elaborated the twelver jurisprudence.[171]
Twelvers constitute the majority of the population in Iran (90%),[172] Azerbaijan (85%),[17][173] Bahrain (70%), Iraq (65%), Lebanon (65% of Muslims).[174][175][176]
Doctrine[edit]

Names of all 12 Imams (descendants of Imam Ali) written in the form of Arabic name على 'Ali'
Twelver doctrine is based on five principles.[177] These five principles known as Usul ad-Din are as follow:[178][179]
Monotheism, God is one and unique.
Justice, the concept of moral rightness based on ethics, fairness, and equity, along with the punishment of the breach of said ethics.
Prophethood, the institution by which God sends emissaries, or prophets, to guide mankind.
Leadership, a divine institution which succeeded the institution of Prophethood. Its appointees (imams) are divinely appointed.
Last Judgment, God's final assessment of humanity.
More specifically, these principles are known as Usul al-Madhhab (principles of the Shia sect) according to Twelver Shias which differ from Daruriyat al-Din (Necessities of Religion) which are principles in order for one to be a Muslim. The Necessities of Religion do not include Leadership (Imamah) as it is not a requirement in order for one to be recognized as a Muslim. However, this category, according to Twelver scholars like Ayatollah al-Khoei, does include belief in God, Prophethood, the Day of Resurrection and other "necessities" (like belief in angels). In this regard, Twelver Shias draw a distinction in terms of believing in the main principles of Islam on the one hand, and specifically Shia doctrines like Imamah on the other.
Books[edit]
Besides the Quran which is common to all Muslims, the Shiah derive guidance from books of traditions ("ḥadīth") attributed to Muhammad and the Twelve Imams. Below is a list of some of the most prominent of these books:
Nahj al-Balagha by Ali ibn Abi Talib – the most famous collection of sermons, letters & narration by the first Imam regarded by Shias
al-Kafi by Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni[180]
- Wasa'il al-Shi'ah by al-Hurr al-Amili
The Twelve Imams[edit]
The Twelve Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad for the Twelvers.[citation needed] According to the theology of Twelvers, the successor of Muhammad is an infallible human individual who not only rules over the community with justice but also is able to keep and interpret the divine law and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the imams are a guide and model for the community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and Imams must be chosen by divine decree, or nass, through Muhammad.[53][54] Each imam was the son of the previous imam, with the exception of Hussein ibn Ali, who was the brother of Hasan ibn Ali.[citation needed] The twelfth and final imam is Muhammad al-Mahdi, who is believed by the Twelvers to be currently alive and in occultation.[57]
Jurisprudence[edit]
The Twelver jurisprudence is called Ja'fari jurisprudence. In this jurisprudence Sunnah is considered to be the oral traditions of Muhammad and their implementation and interpretation by the twelve Imams. There are three schools of Ja'fari jurisprudence: Usuli, Akhbari, and Shaykhi. The Usuli school is by far the largest of the three. Twelver groups that do not follow Ja'fari jurisprudence include Alevi, Bektashi, and Qizilbash.
The five primary pillars of Islam to the Ja'fari jurisprudence, known as Usul' ad-Din. They are at variance with the standard Sunni "five pillars of religion." The Shias' primary "pillars" are:
Tawhid or oneness of God.
Nabuwa prophethood of Muhammad.
Mu'ad resurrection.
Adl justice (of God)
Imama the rightful place of the Shia Imams
In Ja'fari jurisprudence, there are eight secondary pillars, known as Furu' ad-Din, which are as follows:[181]
- Prayer
- Fasting
Pilgrimage to Mecca
- Alms giving
Struggle for the righteous cause- Directing others towards good
- Directing others away from evil
Khums) (20% tax on yearly business earnings after deduction of commercial expenses.)
According to Twelvers, defining and interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence is the responsibility of Muhammad and the twelve Imams. As the 12th Imam is in occultation, it is the duty of clerics to refer to the Islamic literature such as the Quran and hadith and identify legal decisions within the confines of Islamic law to provide means to deal with current issues from an Islamic perspective. In other words, Twelver clerics provide Guardianship of the Islamic Jurisprudence, which was defined by Muhammad and his twelve successors. This process is known as Ijtihad and the clerics are known as Marja', meaning reference. The labels Allamah and Ayatollah are in use for Twelver clerics.
Zaidi ("Fiver")[edit]
Zaidiyya, Zaidism or Zaydi is a Shia school named after Zayd ibn Ali. Followers of the Zaidi fiqh are called Zaidis (or occasionally Fivers). However, there is also a group called Zaidi Wasītīs who are Twelvers (see below). Zaidis constitute roughly 42–47% of the population of Yemen.[182][183]
Doctrine[edit]
The Zaydis, Twelvers, and Ismailis all recognize the same first four Imams; however, the Zaidis recognize Zayd ibn Ali as the fifth. After the time of Zayd ibn Ali, the Zaidis recognized that any descendant of Hasan ibn Ali or Hussein ibn Ali could be imam after fulfilling certain conditions.[184] Other well-known Zaidi Imams in history were Yahya ibn Zayd, Muhammad al-Nafs al-Zakiyya and Ibrahim ibn Abdullah.
The Zaidi doctrine of Imamah does not presuppose the infallibility of the imam nor that the Imams receive divine guidance. Zaidis also do not believe that the Imamate must pass from father to son but believe it can be held by any Sayyid descended from either Hasan ibn Ali or Hussein ibn Ali (as was the case after the death of Hasan ibn Ali). Historically, Zaidis held that Zayd was the rightful successor of the 4th imam since he led a rebellion against the Umayyads in protest of their tyranny and corruption. Muhammad al-Baqir did not engage in political action, and the followers of Zayd believed that a true imam must fight against corrupt rulers.
Jurisprudence[edit]
In matters of Islamic jurisprudence, the Zaydis follow Zayd ibn Ali's teachings which are documented in his book Majmu'l Fiqh (in Arabic: مجموع الفِقه). Al-Hadi ila'l-Haqq Yahya, founder of the Zaydi state in Yemen, instituted elements of the jurisprudential tradition of the Sunni Muslim jurist Abū Ḥanīfa, and as a result, Zaydi jurisprudence today continues somewhat parallel to that of the Hanafis.
Timeline[edit]
The Idrisids (Arabic: الأدارسة) were Arab[185] Zaydi Shia[186][187][188][189][190][191] dynasty in the western Maghreb ruling from 788 to 985 C.E., named after its first sultan, Idris I.
A Zaydi state was established in Gilan, Deylaman and Tabaristan (northern Iran) in 864 C.E. by the Alavids;[192] it lasted until the death of its leader at the hand of the Samanids in 928 C.E. Roughly forty years later the state was revived in Gilan and survived under Hasanid leaders until 1126 C.E. Afterwards, from the 12th to 13th centuries, the Zaydis of Deylaman, Gilan and Tabaristan then acknowledged the Zaydi Imams of Yemen or rival Zaydi Imams within Iran.[193]
The Buyids were initially Zaidi[194] as were the Banu Ukhaidhir rulers of al-Yamama in the 9th and 10th centuries.[195] The leader of the Zaydi community took the title of Caliph. As such, the ruler of Yemen was known as the Caliph, al-Hadi Yahya bin al-Hussain bin al-Qasim ar-Rassi Rassids (a descendant of Hasan ibn Ali the son of Ali) who, at Sa'dah, in 893–7 CE, founded the Zaydi Imamate, and this system continued until the middle of the 20th century, when the revolution of 1962 CE deposed the Zaydi Imam. The founding Zaidism of Yemen was of the Jarudiyya group; however, with increasing interaction with Hanafi and Shafi'i rites of Sunni Islam, there was a shift from the Jarudiyya group to the Sulaimaniyya, Tabiriyya, Butriyya or Salihiyya groups.[196] Zaidis form the second dominant religious group in Yemen. Currently, they constitute about 40–45% of the population in Yemen. Ja'faris and Isma'ilis are 2–5%.[197] In Saudi Arabia, it is estimated that there are over 1 million Zaydis (primarily in the western provinces).
Currently the most prominent Zaydi movement is the Houthis movement, known by the name of Shabab Al Mu'mineen (Believing Youth) or AnsarAllah (Partisans of God). In 2014–2015 Houthis took over the government in Sana'a, which led to the fall of the Saudi Arabian-backed government of Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi.[198] Houthis and their allies gained control of a significant part of Yemen's territory and were resisting the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen seeking to restore Hadi in power. Both the Houthis and the Saudi Arabian-led coalition were being attacked by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.[199][200]
Ismaili[edit]
Ismailis gain their name from their acceptance of Isma'il ibn Jafar as the divinely appointed spiritual successor (Imam) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelvers, who accept Musa al-Kadhim, younger brother of Isma'il, as the true Imam.
After the death or Occultation of Muhammad ibn Ismaill in the 8th century, the teachings of Ismailism further transformed into the belief system as it is known today, with an explicit concentration on the deeper, esoteric meaning (bāṭin) of the faith. With the eventual development of Twelverism into the more literalistic (zahir) oriented Akhbari and later Usuli schools of thought, Shiaism developed in two separate directions: the metaphorical Ismailli group focusing on the mystical path and nature of God and the divine manifestation in the personage of the "Imam of the Time" as the "Face of God", with the more literalistic Twelver group focusing on divine law (sharī'ah) and the deeds and sayings (sunnah) of Muhammad and his successors (the Ahlu l-Bayt), who as A'immah were guides and a light to God.[201]
Though there are several sub-groupings within the Ismailis, the term in today's vernacular generally refers to The Shia Imami Ismaili Muslim (Nizari community), generally known as the Ismailis, who are followers of the Aga Khan and the largest group among the Ismailiyyah. Another community which falls under the Isma'il's are the Dawoodi Bohras, led by a Da'i al-Mutlaq as representative of a hidden imam. While there are many other branches with extremely differing exterior practices, much of the spiritual theology has remained the same since the days of the faith's early Imams. In recent centuries Ismailis have largely been an Indo-Iranian community,[202] but they are found in India, Pakistan, Syria, Palestine, Saudi Arabia,[203] Yemen, China,[204] Jordan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, East Africa and South Africa, and have in recent years emigrated to Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and North America.[205]
Ismaili imams[edit]
After the death of Isma'il ibn Jafar, many Ismailis believed that one day the messianic Mahdi, whom they believed to be Muhammad ibn Ismail, would return and establish an age of justice. One group included the violent Qarmatians, who had a stronghold in Bahrain. In contrast, some Ismailis believed the Imamate did continue, and that the Imams were in occultation and still communicated and taught their followers through a network of dawah "Missionaries".
In 909, Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah, a claimant to the Ismaili Imamate, established the Fatimid Caliphate. During this period, three lineages of imams formed. The first branch, known today as the Druze, began with Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah. Born in 386 AH (985), he ascended as ruler at the age of eleven. The typical religiously tolerant Fatimid Empire saw much persecution under his reign. When in 411 AH (1021) his mule returned without him, soaked in blood, a religious group that was forming in his lifetime broke off from mainstream Ismailism and did not acknowledge his successor. Later to be known as the Druze, they believe al-Hakim to be the incarnation of God and the prophesied Mahdi who would one day return and bring justice to the world.[206] The faith further split from Ismailism as it developed very unusual doctrines which often class it separately from both Ismailiyyah and Islam.
The second split occurred following the death of Ma'ad al-Mustansir Billah in 487 AH (1094). His rule was the longest of any caliph in any Islamic empire. Upon his passing away, his sons, Nizar the older, and Al-Musta'li, the younger, fought for political and spiritual control of the dynasty. Nizar was defeated and jailed, but according to Nizari tradition, his son escaped to Alamut, where the Iranian Ismaili had accepted his claim.[207] From here on, the Nizari Ismaili community has continued with a present, living Imam.
The Mustaali line split again between the Taiyabi (Dawoodi Bohra is its main branch) and the Hafizi. The former claim that At-Tayyib Abi l-Qasim (son of Al-Amir bi-Ahkami l-Lah) and the imams following him went into a period of anonymity (Dawr-e-Satr) and appointed a Da'i al-Mutlaq to guide the community, in a similar manner as the Ismaili had lived after the death of Muhammad ibn Ismail. The latter (Hafizi) claimed that the ruling Fatimid Caliph was the Imam, and they died out with the fall of the Fatimid Empire.
Pillars[edit]
Ismailis have categorized their practices which are known as seven pillars:
|
|
|
|
The Shahada (profession of faith) of the Shia differs from that of Sunnis due to mention of Ali.[208]
Contemporary leadership[edit]
The Nizaris place importance on a scholarly institution because of the existence of a present Imam. The Imam of the Age defines the jurisprudence, and his guidance may differ with Imams previous to him because of different times and circumstances. For Nizari Ismailis, the Imam is Karim al-Husayni Aga Khan IV. The Nizari line of Imams has continued to this day as an unending line.
Divine leadership has continued in the Bohra branch through the institution of the "Unrestricted Missionary" Dai. According to Bohra tradition, before the last Imam, At-Tayyib Abi l-Qasim, went into seclusion, his father, the 20th Al-Amir bi-Ahkami l-Lah, had instructed Al-Hurra Al-Malika the Malika (Queen consort) in Yemen to appoint a vicegerent after the seclusion – the Unrestricted Missionary, who as the Imam's vicegerent has full authority to govern the community in all matters both spiritual and temporal while the lineage of Mustaali-Tayyibi Imams remains in seclusion (Dawr-e-Satr). The three branches of the Mustaali, the Alavi Bohra, Sulaimani Bohra and Dawoodi Bohra, differ on who the current Unrestricted Missionary is.
Other doctrines[edit]
Doctrine about necessity of acquiring knowledge[edit]
According to Allameh Muzaffar, Allah gives humans the faculty of reason and argument. Also, Allah orders humans to spend time thinking carefully on creation while he refers to all creations as his signs of power and glory. These signs encompass all of the universe. Furthermore, there is a similarity between humans as the little world and the universe as the large world. Allah does not accept the faith of those who follow him without thinking and only with imitation, but also Allah blames them for such actions.
In other words, humans have to think about the universe with reason and intellect, a faculty bestowed on us by Allah. Since there is more insistence on the faculty of intellect among Shia, even evaluating the claims of someone who claims prophecy is on the basis of intellect.[209][210]
Doctrine concerning Du'a[edit]
Praying or Du’a in Shia has an important place as Muhammad described it as a weapon of the believer. In fact, Du’a considered as something that is a feature of Shia community in a sense. Performing Du’a in Shia has a special ritual. Because of this, there are many books written on the conditions of praying among Shia. Most of ad’ayieh transferred from Muhammad's household and then by many books in which we can observe the authentic teachings of Muhammad and his household according to Shia. The leaderships of Shia always invited their followers to recite Du’a. For instance, Ali has considered with the subject of Du’a because of his leadership in monotheism.[211][212]
See also[edit]
- Anti-Shi'ism
- Bada'
- Islamic schools and branches
- List of Shia books
- List of Shia Muslim scholars of Islam
- List of Shia Muslims
- List of Shia Islamic dynasties
- Sahabah
- Shia Crescent
- Wudu
- Shi'a view of Ali
References[edit]
^ Olawuyi, Toyib (2014). On the Khilafah of Ali over Abu Bakr. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4928-5884-3. Archived from the original on 22 April 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "The Shura Principle in Islam – by Sadek Sulaiman". www.alhewar.com. Archived from the original on 27 July 2016. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ Triana, María (31 March 2017). Managing Diversity in Organizations: A Global Perspective. Taylor & Francis. p. 159. ISBN 978-1-317-42368-3. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
^ Shi'a is an alternative spelling of Shia, and Shi'ite of Shiite. In subsequent sections, the spellings Shia and Shiite are adopted for consistency, except where the alternative spelling is in the title of a reference.
^ shafaqna.com Shia's population Retrieved 18 Sep 2018
^ "Mapping the Global Muslim Population". 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 14 December 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
^ Newman, Andrew J. (2013). "Introduction". Twelver Shiism: Unity and Diversity in the Life of Islam, 632 to 1722. Edinburgh University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-7486-7833-4.
^ Guidère, Mathieu (2012). Historical Dictionary of Islamic Fundamentalism. Scarecrow Press. p. 319. ISBN 978-0-8108-7965-2.
^ Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam". Oxford University Press, 2002 |
ISBN 978-0-19-515713-0. p. 40
^ "From the article on Shii Islam in Oxford Islamic Studies Online". Oxfordislamicstudies.com. Archived from the original on 28 May 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ Goldziher, I., Arendonk, C. van and Tritton, A.S. (2012). "Ahl al- Bayt". In P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs. Encyclopaedia of Islam (2nd ed.). Brill. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_SIM_0378.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link) CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ "Lesson 13: Imam's Traits". Al-Islam.org. Archived from the original on 9 February 2015.
^ Tabataba'i (1979), p. 76
^ God's rule: the politics of world religions, p. 146, Jacob Neusner, 2003
^ Esposito, John. What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam, Oxford University Press, 2002.
ISBN 978-0-19-515713-0. p.40
^ Duncan S. Ferguson (2010). Exploring the Spirituality of the World Religions: The Quest for Personal, Spiritual and Social Transformation. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 192. ISBN 978-1-4411-4645-8.
^ abcd The New Encyclopædia Britannica, Jacob E. Safra, Chairman of the Board, 15th Edition, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 1998,
ISBN 0-85229-663-0, Vol 10, p. 738
^ Tabataba'i 1977, p. 34
^ Sobhani & Shah-Kazemi 2001, p. 97
^ Sobhani & Shah-Kazemi 2001, p. 98
^ Vaezi 2004, p. 54[citation not found]
^ Cornell 2007, p. 218
^ Cornell 2007, p. 236
^ Momen 1985, p. 15
^ "ʿALĪ B. ABĪ ṬĀLEB". Iranicaonline.org. Archived from the original on 17 May 2015. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
^ abcd Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions, Wendy Doniger, Consulting Editor, Merriam-Webster, Incorporated, Springfield, MA 1999,
ISBN 0-87779-044-2, LoC: BL31.M47 1999, p. 525
^ ab "Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam" Oxford University Press, 2002.
ISBN 978-0-19-515713-0. p. 46
^ Quran 26:214.
^ Razwy, Sayed Ali Asgher. A Restatement of the History of Islam & Muslims. p. 54.
^ Razwy, Sayed Ali Asgher. A Restatement of the History of Islam & Muslims. pp. 54–55.
^ Razwy, Sayed Ali Asgher. A Restatement of the History of Islam & Muslims. p. 55.
^ Irving, Washington. The Life of Mohammed.
^ Burton, Sir Richard (1898). (The Jew the Gypsy and El Islam. San Francisco.
^ Razwy, Sayed Ali Asgher. A Restatement of the History of Islam & Muslims. p. 276.
^ Zakee Kazmee (2011-04-24), "Misconceptions of Shi'a" – Ammar Nakhshwani Lecture at MIT, archived from the original on 2017-04-11, retrieved 2017-04-10
^ Majd, Vahid. The Sermon of Prophet Muhammad (saww) at Ghadir Khum. pp. 17–18.
^ The Last Sermon of Muhammad by Shia Accounts
^ "Search Results - After the death of Allah 's Apostle Fatima the daughter of Allah's Apostle asked Abu Bakr As-Siddiq to give her, her share of inheritance from what Allah's Apostle had (page 1) - Sunnah.com - Sayings and Teachings of Prophet Muhammad (صلى الله عليه و سلم)". Archived from the original on 10 October 2017.
^ "Lesson 8: The Shi'ah among the Companions {sahabah}". Al-Islam.org. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017.
^ "Chapter 3: State of Affairs in Saqifah after the Death of the Prophet". Al-Islam.org. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017.
^ "Did Imam Ali Give Allegiance to Abu Bakr? - Islamic Insights". 8 December 2009. Archived from the original on 28 June 2017.
^ Riz̤vī, Sayyid Sa'eed Ak̲h̲tar. Slavery: From Islamic & Christian Perspectives. Richmond, British Columbia: Vancouver Islamic Educational Foundation, 1988. Print.
ISBN 0-920675-07-7 pp. 35–36
^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2017.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Shaikh, Asif. Sahaba: The Companion. N.p.: n.p., n.d. Print. pp. 42–45
^ Peshawar Nights
^ A list composed of sources such as Ibn Hajar Asqalani and Baladhuri, each in his Ta'rikh, Muhammad Bin Khawind Shah in his Rauzatu's-Safa, Ibn Abdu'l-Birr in his Isti'ab
^ Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, vol. 3, p. 208; Ayoub, 2003, 21
^ The New Encyclopædia Britannica, Jacob E. Safra, Chairman of the Board, 15th Edition, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 1998,
ISBN 0-85229-663-0, Vol 10, p. tid738
^ ""Solhe Emam Hassan"-Imam Hassan Sets Peace". Archived from the original on 11 March 2013.
^ تهذیب التهذیب. p. 271.
^ Discovering Islam: making sense of Muslim history and society (2002) Akbar S. Ahmed
^ Religious trends in pre-Islamic Arabic poetry, By Ghulam Mustafa (Hafiz.), Pg 11, Author writes: Similarly, swords were also placed on the Idols, as it is related that Harith b. Abi Shamir, the Ghassanid king, had presented his two swords, called Mikhdham and Rasub, to the image of the goddess, Manat....to note that the famous sword of Ali, the fourth caliph, called Dhu-al-Fiqar, was one of these two swords
^ ab Nasr (1979), p.10
^ ab Momen 1985, p. 174
^ Corbin 1993, pp. 45–51
^ Nasr (1979), p. 15
^ ab Gleave, Robert. "Imamate". Encyclopaedia of Islam and the Muslim world; vol.1. MacMillan. ISBN 0-02-865604-0.
^ "Learn to do Shia Prayer – Islamic Prayer – Shia Salat". Revertmuslims.com. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ "Joining Prayers and Other Related Issues". Al-islam.org. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ "Druze and Islam". americandruze.com. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
^ "Ijtihad in Islam". AlQazwini.org. Archived from the original on 2 January 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
^ "Shi'ite Islam," by Allamah Sayyid Muhammad Husayn Tabataba'i, translated by Sayyid Husayn Nasr, State University of New York Press, 1975, p. 24
^ Dakake (2008), pp. 1 and 2
^ In his "Mutanabbi devant le siècle ismaëlien de l'Islam", in Mém. de l'Inst Français de Damas, 1935, p.
^ "The Complete Idiot's Guide to World Religions," Brandon Toropov, Father Luke Buckles, Alpha; 3rd edition, 2004,
ISBN 978-1-59257-222-9, p. 135
^ "Shi'ite Islam" by Allamah Sayyid Muhammad Husayn Tabataba'i (1979), pp. 41–44
^ quran 5:55
^ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Verse_of_Wilayah
^ Dabashi, Theology of Discontent, p.463
^ Francis Robinson, Atlas of the Muslim World, p. 47.
^ Quran 33:33
^ Momen 1985, p. 155
^ Corbin (1993), pp. 48 and 49
^ Dabashi (2006), p. 463
^ Corbin (1993), p. 48
^ "Part 1: The Perfect Man". Al-Islam.org. Archived from the original on 17 July 2012.
^ How do Sunnis and Shias differ theologically? Archived 17 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Last updated 2009-08-19, BBC religions
^ Nasr, Sayyed Hossein. "Expectation of the Millennium : Shiìsm in History,", State University of New York Press, 1989, p. 19,
ISBN 978-0-88706-843-0
^ "Comparison of Shias and Sunnis". Religionfacts.com. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ abcd Al-Kulayni, Abu Ja’far Muhammad ibn Ya’qub (2015). Kitab al-Kafi. South Huntington, NY: The Islamic Seminary Inc. ISBN 9780991430864.
^ See: Lapidus p. 47, Holt p. 72
^ Francis Robinson, Atlas of the Islamic World, p. 23.
^ Jafri, S.H. Mohammad. "The Origin and Early Development of Shi'a Islam,", Oxford University Press, 2002, p. 6,
ISBN 978-0-19-579387-1
^ "The Five Kingdoms of the Bahmani Sultanate". orbat.com. Archived from the original on 23 February 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2007.
^ Ansari, N.H. "Bahmanid Dynasty" Archived 19 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Encyclopædia Iranica
^ According to:
Ibn Abī Zarʻ al-Fāsī, ʻAlī ibn ʻAbd Allāh (1340), Rawḍ al-Qirṭās: Anīs al-Muṭrib bi-Rawd al-Qirṭās fī Akhbār Mulūk al-Maghrib wa-Tārīkh Madīnat Fās, ar-Rabāṭ: Dār al-Manṣūr (published 1972), p. 38
- Ignác Goldziher & Bernard Lewis, Introduction to Islamic theology and law, Princeton University Press (1981), p. 218
- James Hastings, Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics, Part 24, Kessinger Publishing (2003), p. 844
Abd Ar Rahman ibn Khaldun (translated by Franz Rosenthal), The Muqaddimah, Chap III : On dynasties, royal authority, the caliphate, government ranks, and all that goes with these things, on www.muslimphilosophy.com
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الأول, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.420
^ Berkey, Jonathan (2003). The Formation of Islam: Religion and Society in the Near East, 600-1800. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-58813-3., p. 135
^ ab Newman, Andrew J. Twelver Shiism: Unity and Diversity in the Life of Islam, 632 to 1722. Edinburgh University Press, Nov 20, 2013.
^ RM Savory, Safavids, Encyclopedia of Islam, 2nd ed.
^ ab Yitzhak Nakash, Reaching for Power:The Shi'a in the Modern Arab World, (Princeton University Press, 2006), 22.
^ http://www.alwasatnews.com/data/2009/2379/pdf/fdt5.pdf
^ Juan R. I. Cole, "Rival Empires of Trade and Imami Shiism in Eastern Arabia, 1300-1800", International Journal of Middle East Studies, Vol. 19, No. 2. (May, 1987), pp. 177-203, at p. 179, through JSTOR. [1]
^ Antiquity to Institutionalization of al-Khalifa Rule. Fanack. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
^ Contemporary Yemen: politics and historical background, By B. R. Pridham, pg.14
^ "Al-Humaydi and Peter Scales (1994: 94-95) seem to be ignorant of the Zaydiyya, whose outward practice appears Sunni. Possibly, Al-Humaydi and Scales have conflated Shi'ite with Imamiyyah and are in fact refuting their projection of the Hammudids." Article by Sayyid 'Ali ibn 'Ali Al-Zaidi, At-tarikh as-saghir 'an ash-shia al-yamaniyeen (Arabic: التاريخ الصغير عن الشيعة اليمنيين, A short History of the Yemenite Shi‘ites). 2005
^ http://www.talpur.org
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1987
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1987
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1987
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1987
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1987
^ شاكر مصطفى, موسوعة دول العالم الأسلامي ورجالها الجزء الثالث, (دار العلم للملايين: 1993), p.1360
^ Pollard, Elizabeth (2015). Worlds Together Worlds Apart. 500 Fifth Ave, NY: W.W. Norton Company Inc. p. 313. ISBN 978-0-393-91847-2.
^ Gábor Ágoston; Bruce Alan Masters (2010). Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire. Infobase Publishing. p. 71. ISBN 978-1-4381-1025-7.
^ Stanford J. Shaw; Ezel Kural Shaw (1976). History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey: Volume 1, Empire of the Gazis: The Rise and Decline of the Ottoman Empire 1280–1808. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29163-7.
^ Francis Robinson, Atlas of the Muslim World, p. 49.
^ Momen 1985, p. 123
^ Momen 1985, pp. 191, 130
^ "Discrimination towards Shia in Saudi Arabia". Wsws.org. 8 October 2001. Archived from the original on 12 May 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ Momen 1985, p. 277
^ "Religions". CIA. The World Factbook. 2010. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
^ "Shīʿite". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2010. Archived from the original on 9 August 2010. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
^ abcdefghij "Mapping the Global Muslim Population: A Report on the Size and Distribution of the World's Muslim Population". Pew Research Center. 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 14 December 2015. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
^ abcdefg
Miller, Tracy, ed. (October 2009). Mapping the Global Muslim Population: A Report on the Size and Distribution of the World's Muslim Population (PDF). Pew Research Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2010. Retrieved 2009-10-08.
^ ab "Foreign Affairs – When the Shiites Rise – Vali Nasr". Mafhoum.com. Archived from the original on 15 January 2014. Retrieved 27 January 2014.
^ "Quick guide: Sunnis and Shias". BBC News. 11 December 2006. Archived from the original on 28 December 2008.
^ Written at U.S.A. Atlas of the Middle East (Second ed.). Washington D.C.: National Geographic. 15 April 2008. pp. 80–81. ISBN 978-1-4262-0221-6.
^ "International Religious Freedom Report 2010". U.S. Government Department of State. Archived from the original on 13 July 2013. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
^ "How many Shia?". Islamicweb.com. Archived from the original on 25 May 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ ab "International Religious Freedom Report for 2012". US State Department. 2012. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017.
^ ab "The New Middle East, Turkey, and the Search for Regional Stability" (PDF). Strategic Studies Institute. April 2008. p. 87. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 March 2015.
^ Shankland, David (2003). The Alevis in Turkey: The Emergence of a Secular Islamic Tradition. Routledge (UK). ISBN 0-7007-1606-8.
^ "Country Profile: Pakistan" (PDF). Library of Congress Country Studies on Pakistan. Library of Congress. February 2005. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 July 2005. Retrieved 1 September 2010.Religion: The overwhelming majority of the population (96.3 percent) is Muslim, of whom approximately 95 percent are Sunni and 5 percent Shia.
^ ab "Shia women too can initiate divorce" (PDF). Library of Congress Country Studies on Afghanistan. August 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 2010-08-27.Religion: Virtually the entire population is Muslim. Between 80 and 85 percent of Muslims are Sunni and 15 to 19 percent, Shia.
^ "Afghanistan". Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). The World Factbook on Afghanistan. Archived from the original on 28 May 2010. Retrieved 27 August 2010.Religions: Sunni Muslim 80%, Shia Muslim 19%, other 1%
^ al-Qudaihi, Anees (24 March 2009). "Saudi Arabia's Shia press for rights". BBC Arabic Service. Archived from the original on 7 April 2010. Retrieved 24 March 2009.
^ Leonard Leo. International Religious Freedom (2010): Annual Report to Congress. Diane Publishing. pp. 261–. ISBN 978-1-4379-4439-6. Retrieved 24 October 2012.
^ Paul Ohia (16 November 2010). "Nigeria: 'No Settlement With Iran Yet'". This Day. Archived from the original on 18 October 2012.
^ Helene Charton-Bigot, Deyssi Rodriguez-Torres. Nairobi Today. the Paradox of a Fragmented City. African Books Collective, 2010.
ISBN 9987-08-093-6,
ISBN 978-9987-08-093-9. Pg 239
^ Heinrich Matthée (2008). Muslim Identities and Political Strategies: A Case Study of Muslims in the Greater Cape Town Area of South Africa, 1994–2000. kassel university press GmbH. pp. 136–. ISBN 978-3-89958-406-6. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
^ Mohamed Diriye Abdullahi. Culture and customs of Somalia. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001.
ISBN 0-313-31333-4,
ISBN 978-0-313-31333-2. Pg 55
^ Yasurō Hase; Hiroyuki Miyake; Fumiko Oshikawa (2002). South Asian migration in comparative perspective, movement, settlement and diaspora. Japan Center for Area Studies, National Museum of Ethnology.
^ abcd Husain, Rahat (26 October 2015). "Analysis indicates Shia populations are being underreported". Communities Digital News. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Archived from the original on 3 February 2012.
^ "CIA – The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 3 July 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ "Violence Against Pakistani Shias Continues Unnoticed | International News". Islamic Insights. Archived from the original on 12 May 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ "Taliban kills Shia school children in Pakistan". Archived from the original on 12 May 2011.
^ "Shia women too can initiate divorce". The Times of India. 6 November 2006. Archived from the original on 25 March 2014. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
^ "30,000 Indian Shia Muslims Ready to Fight Isis 'Bare Handed' in Iraq". International Business Times UK. Archived from the original on 16 January 2015.
^ "Religion" (PDF). Administrative Department of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan – Presidential Library. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 August 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
^ "'No Settlement with Iran Yet'". This Day. 16 November 2010. Archived from the original on 2013-05-28.
^ "Shia Population in Bangladesh". World Shia Muslims Population. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
^ Growth of the world's urban and rural population:n1920-2000, Page 81. United Nations. Dept. of Economic and Social Affairs
^ Hassan, Farzana. Prophecy and the Fundamentalist Quest, page 158
^ Corstange, Daniel M. Institutions and Ethnic politics in Lebanon and Yemen, page 53
^ Dagher, Carole H. Bring Down the Walls: Lebanon's Post-War Challenge, page 70
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2 February 2012. Retrieved 2012-03-03.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Why Bahrain blew up". New York Post. 17 February 2011. Archived from the original on 4 October 2012. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
^ Top 15 Countries with Highest Proportion of Shiites in the Population Archived 7 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine., 7 July 1999
^ (Ya'qubi; vol. III, pp. 91–96, and Tarikh Abul Fida', vol. I, p. 212.)
^ Stevan Lars Nielson, PhD; E. Thomas Dowd, PhD, ABPP (2006). The Psychologies in Religion: Working with the Religious Client. Springer Publishing Company. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-8261-2857-7.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ "Basra handover completed". Inthenews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 1 August 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ Maddox, Bronwen (2006-12-30). "Hanging will bring only more bloodshed". The Times. London. Retrieved 2010-05-23.
^ "Al-Ahram Weekly | Region | Shi'ism or schism". Weekly.ahram.org.eg. 17 March 2004. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ The Shia, Ted Thornton, NMH, Northfield Mount Hermon Archived 13 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "The Origins of the Sunni/Shia split in Islam". Islamfortoday.com. Archived from the original on 26 January 2007. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ Nasr, Vali (2006). The Shia Revival: How Conflicts Within Islam Will Shape the Future. W.W. Norton & Company Inc.
ISBN 978-0-393-06211-3 p. 52-53
^ George C. Kohn (2007.) Dictionary of Wars. Infobase Publishing. p.385.
ISBN 0-8160-6577-2
^ Al-e Ahmad, Jalal. Plagued by the West (Gharbzadegi), translated by Paul Sprachman. Delmor, NY: Center for Iranian Studies, Columbia University, 1982.
^ Saudi Arabia – The Saud Family and Wahhabi Islam Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Library of Congress Country Studies.
^ Gritten, David (25 February 2006). "Long path to Iraq's sectarian split". BBC News. Archived from the original on 27 July 2008. Retrieved 19 April 2015.
^ "Malaysian government to Shia Muslims: Keep your beliefs to yourself". globalpost.com. Archived from the original on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
^ "Malaysia" (PDF). state.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 September 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
^ Paula Sanders (1994), Ritual, politics, and the city in Fatimid Cairo, p.121
^ Bernard Trawicky, Ruth Wilhelme Gregory, (2002), Anniversaries and holidays, p.233
^ "Mawlid al-Nabi (the Prophet's birthday)". Islamqa.info. Archived from the original on 26 December 2015. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
^ "Lady Fatima inspired women of Iran to emerge as an extraordinary force". 18 March 2017.
^ Laurence Louėr (2008), Transnational Shia politics: religious and political networks in the Gulf, p.22
^ Karen Dabrowska, Geoff Hann, (2008), Iraq Then and Now: A Guide to the Country and Its People, p.239
^ Cornell 2007, p. 237
^ "Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam" Oxford University Press, 2002.
ISBN 978-0-19-515713-0. p. 45.
^ "Administrative Department of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan – Presidential Library – Religion" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 August 2011.
^ Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam" Oxford University Press, 2002.
ISBN 978-0-19-515713-0. p. 45
^ John Pike. "Bahrain – Religion". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012.
^ "Challenges For Saudi Arabia Amidst Protests In The Gulf – Analysis". Eurasia Review. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012.
^ "Shiʿite Doctrine". iranicaonline.org. Archived from the original on 17 May 2015.
^ Joanne Richter, (2006), Iran the Culture, p.7
^ Mulla Bashir Rahim, An Introduction to Islam Archived 14 October 2009 at the Portuguese Web Archive, by Ahlul Bayt Digital Islamic Library Project
^ Islamic Texts Institute (2012). Al-Kafi Book I: Intellect and Foolishness. Taqwa Media. ISBN 978-1-939420-00-8.
^ Iran the Culture Joanne Richter (2007), p.7
^ "About Yemen". Yemeni in Canada. Embassy of the Republic of Yemen in Canada. Archived from the original on 27 January 2007. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
^ "Yemen [Yamaniyyah]: general data of the country". Population Statistics. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
^ Sunni-Shi'a Schism: Less There Than Meets the Eye Archived 23 April 2005 at the Library of Congress Web Archives 1991 Page 24
^ Hodgson, Marshall (1961). "Venture of Islam". Chicago: University of Chicago Press: 262.
^ Ibn Abī Zarʻ al-Fāsī, ʻAlī ibn ʻAbd Allāh (1340). "Rawḍ al-Qirṭās: Anīs al-Muṭrib bi-Rawd al-Qirṭās fī Akhbār Mulūk al-Maghrib wa-Tārīkh Madīnat Fās". ar-Rabāṭ: Dār al-Manṣūr (published 1972): 38.
^ "حين يكتشف المغاربة أنهم كانوا شيعة وخوارج قبل أن يصبحوا مالكيين !". hespress.com. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008.
^ Ignác Goldziher (1981). Introduction to Islamic Theology and Law. Princeton University Press. p. 218. ISBN 0-691-10099-3.
^ James Hastings (2003). Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics. Kessinger Publishing. p. 844. ISBN 978-0-7661-3704-2.
^ "The Institute of Ismaili Studies - The Initial Destination of the Fatimid caliphate: The Yemen or The Maghrib?". iis.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 6 July 2015.
^ "Shi'ah tenets concerning the question of the imamate – New Page 1". muslimphilosophy.com. Archived from the original on 29 August 2012.
^ Article by Sayyid 'Ali ibn 'Ali Al-Zaidi,At-tarikh as-saghir 'an ash-shia al-yamaniyeen (Arabic: التاريخ الصغير عن الشيعة اليمنيين, A short History of the Yemenite Shi‘ites), 2005 Referencing: Iranian Influence on Moslem Literature
^ Article by Sayyid 'Ali ibn 'Ali Al-Zaidi, At-tarikh as-saghir 'an ash-shia al-yamaniyeen (Arabic: التاريخ الصغير عن الشيعة اليمنيين, A short History of the Yemenite Shi‘ites), 2005 Referencing: Encyclopædia Iranica
^ Walker, Paul Ernest (1999). Hamid Al-Din Al-Kirmani: Ismaili Thought in the Age of Al-Hakim. Ismaili Heritage Series. 3. London ; New York: I.B. Tauris in association with the Institute of Ismaili Studies. p. 13. ISBN 1-86064-321-3.
^ Madelung, W. "al-Uk̲h̲ayḍir." Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2007. Brill Online. 7 December 2007 (registration required)
^ Article by Sayyid Ali ibn ' Ali Al-Zaidi, At-tarikh as-saghir 'an ash-shia al-yamaniyeen (Arabic: التاريخ الصغير عن الشيعة اليمنيين, A short History of the Yemenite Shi‘ites), 2005
^ "Universiteit Utrecht Universiteitsbibliotheek". Library.uu.nl. Archived from the original on 2 May 2006. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ "Yemen's Houthis form own government in Sanaa". Al Jazeera. 6 February 2015. Archived from the original on 7 February 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
^ "Yemen govt vows to stay in Aden despite IS bombings". Yahoo News. 7 October 2015. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015.
^ "Arab Coalition Faces New Islamic State Foe in Yemen Conflict". NDTV.com. 7 October 2015. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
^ "Shaykh Ahmad al-Ahsa'i". Archived from the original on 18 February 2007. Retrieved 25 April 2007.
^ Nasr, Vali, The Shia Revival, Norton, (2006), p. 76
^ "Congressional Human Rights Caucus Testimony – NAJRAN, The Untold Story". Archived from the original on 27 December 2006. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
^ "News Summary: China; Latvia". Archived from the original on 6 May 2007. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
^ Daftary, Farhad (1998). A Short History of the Ismailis. Edinburgh, UK: Edinburgh University Press. pp. 1–4. ISBN 0-7486-0687-4.
^ "al-Hakim bi Amr Allah: Fatimid Caliph of Egypt". Archived from the original on 6 April 2007. Retrieved 24 April 2007.
^ Daftary, Farhad (1998). A Short History of the Ismailis. Edinburgh, UK: Edinburgh University Press. pp. 106–108. ISBN 0-7486-0687-4.
^ "Encyclopedia of the Middle East". Mideastweb.org. 14 November 2008. Archived from the original on 12 May 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
^ Allamah Muhammad Rida Al Muzaffar (1989). The faith of Shia Islam. Ansariyan Qum. p. 1.
^ "The Beliefs of Shia Islam – Chapter 1". Archived from the original on 25 October 2016.
^ "The Beliefs of Shia Islam – Chapter 5.1". Archived from the original on 25 October 2016.
^ Allamah Muhammad Rida Al Muzaffar (1989). The faith of Shia Islam. Ansariyan Qum. pp. 50–51.
Bibliography[edit]
Cornell, Vincent J. (2007). Voices of Islam. Westport, Conn.: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 978-0-275-98732-9.
Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Encyclopædia Iranica. Center for Iranian Studies, Columbia University. ISBN 1-56859-050-4.
Martin, Richard C. Encyclopaedia of Islam and the Muslim world; vol.1. MacMillan. ISBN 0-02-865604-0.
Corbin, Henry (1993) [1964]. History of Islamic Philosophy, Translated by Liadain Sherrard, Philip Sherrard. London; Kegan Paul International in association with Islamic Publications for The Institute of Ismaili Studies. ISBN 0-7103-0416-1.
Dakake, Maria Massi (2008). The Charismatic Community: Shi'ite Identity in Early Islam. Suny Press. ISBN 0-7914-7033-4.
Holt, P. M.; Lewis, Bernard (1977a). Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-29136-4.
Lapidus, Ira (2002). A History of Islamic Societies (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77933-3.
Momen, Moojan (1985). An Introduction to Shi'i Islam: The History and Doctrines of Twelve. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-03531-4.
Sachedina, Abdulaziz Abdulhussein (1988). The Just Ruler (al-sultān Al-ʻādil) in Shīʻite Islam: The Comprehensive Authority of the Jurist in Imamite Jurisprudence. Oxford University Press US. ISBN 0-19-511915-0.
Sobhani, Ja'afar; Shah-Kazemi, Reza (2001). Doctrines of Shiʻi Islam: a Compendium of Imami Beliefs and Practices ([Online-Ausg.] ed.). London: I.B. Tauris [u.a.] ISBN 978-1-86064-780-2.
Tabatabaei, Sayyid Mohammad Hosayn (1979). Shi'ite Islam. Translated by Seyyed Hossein Nasr. Suny press. ISBN 0-87395-272-3.
Ṭabataba'i, Allamah Sayyid Muḥammad Husayn (1977). Shiʻite Islam. Albany: State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-0-87395-390-0.
Further reading[edit]
- Peter J. Chelkowski (ed.), Eternal Performance: Taziyah and Other Shiite Rituals (Salt lake City (UT), Seagull Books, 2010) (Seagull Books - Enactments).
Corbin, Henry (1993). History of Islamic Philosophy, translated by Liadain Sherrard and Philip Sherrard. Kegan Paul International in association with Islamic Publications for The Institute of Ismaili Studies. ISBN 0-7103-0416-1.
Dabashi, Hamid (2011). Shi'ism: A Religion of Protest. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-06428-7.
Halm, Heinz (2004). Shi'ism. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 0-7486-1888-0.
Halm, Heinz (2007). The Shi'ites: A Short History. Markus Wiener Pub. ISBN 1-55876-437-2.
Lalani, Arzina R. (2000). Early Shi'i Thought: The Teachings of Imam Muhammad Al-Baqir. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 1-86064-434-1.
- Marcinkowski, Christoph (2010). Shi'ite Identities: Community and Culture in Changing Social Contexts, Lit Verlag 2010. ISBN 978-643-3- 80049-7.
Momen, Moojan (1985). An Introduction to Shi'i Islam: The History and Doctrines of Twelver Shi'ism. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-03499-7.
Shirazi, Sultanu'l-Wa'izin. Peshawar Nights, A Transcript of a Dialogue between Shia and Sunni scholars. Ansariyan Publications. ISBN 978-964-438-320-5.
Nasr, Seyyed Hossein; Hamid Dabashi (1989). Expectation of the Millennium: Shiʻism in History. SUNY Press. ISBN 0-88706-843-X.
Rogerson, Barnaby (2007). The Heirs of Muhammad: Islam's First Century and the Origins of the Sunni Shia split. Overlook Press. ISBN 1-58567-896-1.
Wollaston, Arthur N. (2005). The Sunnis and Shias. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 1-4254-7916-2.
Moosa, Matti (1988). Extremist Shiites: The Ghulat Sects. Syracuse University Press. ISBN 0-8156-2411-5.
External links[edit]
Wikisource has the text of the 1905 New International Encyclopedia article Shiites. |
Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Shi'ites. |
- World Best & Biggest Shia Community Social Network
- Library of Shia Muslims Videos
- Shafaqna: International Shia News Agency
- English language website
- YaHusain.com, Shia Website with informative lectures in English & Urdu
- Islamic – Shia Website
- Al-Islam.org, A Digital Islamic Library
- The Shiapedia, an online Shia encyclopedia
- Murajaat – A Shi'i/Sunni debate
- Patheos Library – Shi'a Islam
- shiasource.com
Imam Al-Khoei Foundation (Twelver)
Official Website of Nizari Ismaili (Ismaili)
Official Website of Alavi Bohra (Ismaili)
Dawoodi Bohra (Ismaili)
The Institute of Ismaili Studies (Ismaili)
Shia at Curlie
al-shia.org Ahlulbayt Global Informations Center
Categories:
- Shia Islam
(window.RLQ=window.RLQ||).push(function(){mw.config.set({"wgPageParseReport":{"limitreport":{"cputime":"2.648","walltime":"3.092","ppvisitednodes":{"value":32639,"limit":1000000},"ppgeneratednodes":{"value":0,"limit":1500000},"postexpandincludesize":{"value":656997,"limit":2097152},"templateargumentsize":{"value":24897,"limit":2097152},"expansiondepth":{"value":13,"limit":40},"expensivefunctioncount":{"value":15,"limit":500},"unstrip-depth":{"value":1,"limit":20},"unstrip-size":{"value":422148,"limit":5000000},"entityaccesscount":{"value":2,"limit":400},"timingprofile":["100.00% 2386.249 1 -total"," 39.17% 934.591 2 Template:Reflist"," 12.52% 298.688 54 Template:Cite_book"," 12.02% 286.853 67 Template:Cite_web"," 11.00% 262.405 14 Template:Navbox"," 8.57% 204.397 1 Template:Asia_topic"," 6.93% 165.319 56 Template:Iso2country"," 6.79% 162.073 3 Template:Lang-ar"," 4.83% 115.240 18 Template:ISBN"," 3.44% 81.990 3 Template:Navbox_with_collapsible_groups"]},"scribunto":{"limitreport-timeusage":{"value":"1.133","limit":"10.000"},"limitreport-memusage":{"value":26193889,"limit":52428800}},"cachereport":{"origin":"mw1278","timestamp":"20181112044126","ttl":1900800,"transientcontent":false}}});mw.config.set({"wgBackendResponseTime":147,"wgHostname":"mw1238"});});




